How to train the vestibular apparatus at home (video). A set of exercises for therapeutic vestibular gymnastics
There is an effective a set of exercises for training and developing the vestibular apparatus and balance . It is suitable for children, young active people, and the elderly - the only difference is the degree of intensity when performing a set of exercises.
Older people should be extremely careful when performing the complex: increase the load gradually and train next to a reliable support (for example, a wall bar), which you can always grab onto if you lose balance. Each exercise is performed 5-10 times depending on your health condition.
1. Starting position (ip.) – standing, arms in front of the chest, elbows bent. Jerks your arms back on the count of 1,2,3, on the count of 4 – spread your straight arms to the sides.
2. I.p. – standing, hands on your belt, legs together. Without lifting your feet from the floor, lift the toe of your right foot and the heel of your left foot, then vice versa.
3. I.p. – standing, arms along the body. Slow body tilts to the right and left.
4. I.p. - Same. Raise your right leg bent at the knee, straighten it, bend it again, lower it to the floor. Repeat the exercise with your left leg. Perform with support at first to maintain stability.
5. I.p. - Same. Alternately move your arms to the side while turning your body in the same direction, while looking at the fingers of the abducted hand.
6. "Swallow". I.p. - Same. Lean forward while raising your leg and arms to the sides. Be sure to hold onto the support with your hand at first.

7. I.p. – standing, feet shoulder-width apart, ball in hands. Throw the ball at different heights and try to catch it. While performing the exercise, watch the flight of the ball.
8. I.p. Same. Hit the ball against the wall, let it hit the floor once or twice, turn around during this time and catch the ball.
9. I.p. – standing, hands on the belt. Walking alternately on your toes and heels: two steps on your toes, two steps on your heels.

10. I.p. – standing, arms along the body. Walk with an extended step, after four steps, turn in a circle over the right and left shoulders alternately.
11. I.p. - Same. When walking: take two steps - one hand to the side, the other - up. In the next two steps, the position of the hands changes. The exercise can be made more difficult by turning your head and following one of your hands with your eyes.

12. I.p. - Same. Walk with an ordinary step forward and backward (without turning around), first with your eyes open, then with your eyes closed.
13. I.p. - Same. Stretch your arms forward. With one hand, make free movements in front of the chest, and with the other hand, simultaneously outline a triangle.
14. I.p. - Same. Stretch your arms forward. At the same time, describe circles clockwise with one hand and counterclockwise with the other. To complicate the exercise, you can draw a square with your foot at the same time.

15. I.p. – standing, one hand on your belt, the other holding on to the support, eyes closed. Rise on your toes, stand for 15 seconds, trying to maintain balance, and return to the starting position. Then, also holding onto the support and without opening your eyes, stand on your toes, try to raise your leg and maintain your balance.
16. I.p. – standing, hands on the belt. Rise onto your toes and make several careful circular movements with your head. Close your eyes and do the same exercise. I.p. - Same. Holding the support, perform alternate circular swings with your legs. To complicate the exercise, perform circular swings with one leg, rising on the toe of the other leg.
17. I.p. - Same. Holding the support, perform alternate circular swings with your legs. To complicate the exercise, perform circular swings with one leg, rising on the toe of the other leg.

It's also useful to know how to train the vestibular apparatus , develop coordination of movements And sense of balance through games. All this can be done in a playful and even humorous form by throwing a tennis ball at a target, throwing a ball into a basketball basket, or walking on a fairly narrow (about 15 cm) board lying on the floor.
How I strengthened the vestibular apparatus using simple methods accessible to everyone. Since childhood I have suffered in transport. Doctors said it was a weak vestibular system. Especially in the morning, if you need to go somewhere by bus or car, it’s a disaster. I have long set a goal to strengthen the vestibular apparatus. But it turns out that his training is necessary.
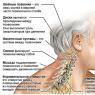
VESTIBULAR APPARATUS , an organ of balance, a receptor apparatus that helps orient the body in space and maintain its balance at rest and during movement. The vestibular apparatus is located in the inner ear.
A person receives information through five main senses: eyes - vision, ears - hearing, tongue - taste, nose - smell, skin - touch. There is a sixth sense: the vestibular apparatus - a sense of balance and position in space.
The vestibular apparatus consists of a collection of sensory hair-like cells. Hair cells are located on the bony ridges of the enlarged parts of the semicircular canals - the ampullae. Endolymph is an intratubular fluid containing “calcareous pebbles” - otoliths and a jelly-like mass - cupules.
Over time, I noticed that if the car drives without strong changes in movement, i.e. straight up, no problem. If there are frequent turns, braking, and U-turns, I feel bad, I feel sick. What's going on?
When the position of the body changes or its movement in the vestibular apparatus, irritation of sensitive hairs occurs. During angular accelerations, for example, when turning and tilting the head and body - due to the inertial displacement of the endolymph in relation to them. With linear accelerations and changes in gravity, for example, horizontal or vertical movement - flying in an airplane, climbing an elevator - due to the movement of otoliths.
The oval sac, the utriculus, which is part of the vestibular apparatus, connects the semicircular canals and is involved in the perception of body position and, probably, in the sensation of rotation. The round pouch, the sacculus, complements the oval one and, apparently, perceives vibrations.
The excitation that occurs when sensitive cells are irritated is transmitted from them along the vestibular branch of the auditory nerve to the central nervous system, and from there to the muscles. This causes a coordinated change in their tone and allows a person to maintain balance when changing body position, even with his eyes closed.
If irritations of the vestibular apparatus are strong and last long enough, then some people may experience disturbances in its function, manifested by the so-called symptom complex of “motion sickness.” This manifests itself as dizziness, disturbances in cardiac activity, breathing rhythm, nausea, vomiting, loss of balance. An example can be given of seasickness while sailing on a ship or boating.
And of course, to normalize the function of the vestibular apparatus, which means it is necessary to train it. To do this you should do special sets of physical exercises.
You should exercise daily, even when the attacks of dizziness stop, to prevent relapses. The duration of the complex will not take much time - 10-15 minutes.
For some people, training may initially increase dizziness and cause tinnitus. However, they must be continued, gradually increasing the load. After 3-4 months of training, attacks of dizziness and nausea in moving vehicles occur less frequently and health improves. The same thing happened to me.
Systematic training helps to completely get rid of the unpleasant sensations that cloud travel and trips.
A set of exercises performed while sitting on a chair, from the starting position - legs straight, heels straight together, arms down.
1. Tilt your head down - exhale, raise your head up - inhale.
2. Turn your head left, right.
3. Tilt your head to the left shoulder, straighten it, and do the same to the right shoulder.
4. Circular movement of the head from left to right, the same from right to left, lowering the head - exhale, raising it - inhale.
After 10 days, additional exercises 5-7 are introduced, from the starting position - legs wider than shoulders, arms down.
5. Inhale, exhale, bend towards your left leg, reach for it with your hands, return to the starting position, the same for the right leg.
6. Hands on the belt - inhale, turn the torso to the right - exhale, do the same to the left.
7. Take the seat of the chair with your hands, move your torso back - inhale, return to the starting position - exhale. Each exercise should be repeated 5-10 times, smoothly, without jerking, breathing in exercises 1 and 5 is rhythmic, through the nose or voluntary.
After 10 days, if you feel well, this set of exercises is performed in a standing position, feet shoulder-width apart, holding the back of a chair with your hand.
After 20 days, if there is no dizziness, you can go to the starting position, standing without support, feet wider than shoulders, arms down, and add exercises numbered 8-10.
8. Raise your hands up - inhale, bend forward, trying to touch the floor with your hands - exhale, rhythmic breathing through the nose, first with your eyes open, then with your eyes closed.
9. Hands on the belt, rotating the body to the right, then to the left, bending the body down - exhale, straightening - inhale.
10. Clench your hands into fists and bend at the elbows, throw your right hand forward and to the left with force (at the same time, the head and torso make a half-turn to the left), when the right hand returns to its original position, throw out the left one with force, breathing is arbitrary, first perform it with open eyes, then closed.
Each exercise should be performed 5-10 times.
After mastering the exercises, walking is included in the gymnastic complex.
11. You should walk 2 m forward and, without turning around, walk the same amount back (repeat 2 times).
12. They walk first with their eyes open, then with their eyes closed, and back away with their eyes open.
Having achieved stability, they begin to walk with their eyes closed, both forward and backward. Gradually the number of repetitions is increased to 10 times.
You can train the vestibular apparatus on a homemade simulator.
A very simple, accessible method was suggested by a neighbor on the landing, who one morning dropped me off at work and, naturally, I felt unwell.
A “Grace” rotation disc is placed on a stool, preferably with a round seat. That's the whole simulator.
The seat and disc are held together by a metal axle with a threaded nut at the bottom. This allows you to adjust the degree of ease of rotational movements. Perform 2-3 rotations in any direction several times a day, gradually increasing the number of rotations.
Another very light and affordable exercise machine is a rocking chair. Rocking in a rocking chair also helps train the vestibular system.
A number of professions and sports place increased demands on the vestibular apparatus, which, even with a fairly high function, can only be satisfied through systematic training according to special schemes and with special equipment (for example, in circus arts, flying, astronautics, acrobatics, etc. ).
Don’t be lazy, train daily and after a while you will achieve success and strengthen your vestibular apparatus. I wish you good luck.

The vestibular apparatus is an organ that perceives changes in the positions of the head and body in space.
This organ is located in the inner part of the ear.
With poor development of the vestibular system, a person experiences nausea, vomiting, disturbances in consciousness, fainting and dizziness when changing position.
At a young age, such manifestations are rarely observed, but as a person ages, changes occur in the body that disrupt the functioning of this organ, so it becomes more susceptible to any changes in the coordination of human movements.
To enhance sensitivity, it is worth doing vestibular exercises for older people.
Gymnastics for the vestibular apparatus is a set of simple exercises that older people can do at home.
It is worth remembering that such exercises are aimed at concentrating your attention, and not at training the muscles of the body.
All older people are allowed to practice this type of gymnastics to correct their balance.

But exercises are directly indicated for people who suffer from:
- Post-stroke period.
- Positional paroxysmal vertigo.
- General disturbances in coordination of movements.
- Osteochondrosis.
- From damage to the spinal column.
- Discirculatory encephalopathy.
- Pathologies of the ear area.
This set of classes is also necessary for people who have suffered a traumatic brain injury in the past.
The effect of gymnastics
Vestibular gymnastics exercises have the following effect:
- Reducing the likelihood of injury from a fall.
- Reduced symptoms of nausea and dizziness.
- Increased blood flow to the brain organs.
- Improving quality of life.
- Balance coordination.
- Improved vision.
For older people, the problem of orientation in space and maintaining balance remains relevant, and therapeutic exercises for the vestibular apparatus help solve this problem.
Exercises not only strengthen the organ, but also prepare the body for possible falls so that the person receives a minimum of injuries.
Contraindications
Vestibular gymnastics at home is undoubtedly beneficial for the body, but before performing the exercises you should definitely consult a doctor, since exercises have a number of contraindications that not only will not help, but can also aggravate a person’s already serious condition.
- Respiratory rhythm disturbance.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Period of colds or infectious diseases.
Training rules
All classes are carried out in comfortable clothing.
It should not put pressure on any parts of the body or organs, as during training, blood circulation may be disrupted or worsened.
All exercises should be performed slowly, the pace of execution gradually increasing.
Classes are usually held for a minimum of 2 hours with a mandatory interval of at least 8 hours. The training course usually takes 2 months.
Set of exercises
To strengthen the vestibular system, you can perform the following exercises.
Stand up straight, put your feet together, bend your torso and arms forward as much as possible.
Then the back is slowly straightened, and the arms are raised above the head and folded with palms facing each other. This position should be fixed for 5 – 10 seconds.
Stand upright. Raise your right leg, hold for 5 – 8 seconds, then repeat the actions with your left leg.
In a standing position, the head leans forward until the chin touches the chest.

Then, in this position, bends are made to the right and left sides. The goal is to reach your ear with your shoulder. Rotating your head clockwise and counterclockwise is very effective.
Sit on a chair, gradually raise and lower your shoulders without lowering or tilting your head. Stand up straight, place your feet shoulder-width apart, and lower your arms. Bend to the left and right.
The following exercise is intended for people with good physical fitness. You will need to sit on the floor, stretch your legs in front of you.
Then you need to quickly lie down and roll over onto your left side. The gaze is directed straight ahead. After this, a rollover is carried out on the right side. Then the person needs to lie on his back and take the starting position.
For dizziness
Vestibular gymnastics after a stroke involves performing exercises for the head, which improves blood flow and increases the supply of oxygen to brain cells.
This vestibular exercise helps with dizziness and frequent headaches. All exercises are performed with open eyes.
Stand on your feet, straighten your back, do rotations and lifts with your arms. The person should feel that the main load falls on the shoulder joints.
Stand up straight and place in front of you any object (not heavy)

then slowly lower your torso forward and lift the object with straightened arms. Then you should sit down with the object. This exercise is repeated at least 20 times.
Sit down on a flat surface with your legs extended in front of you. Then stand up slowly. Pick up a non-bulky, light object. Stretch your arms in front of you. Transfer it from hand to hand.
Brandt-Daroff gymnastics is particularly effective. After waking up, you should sit on the bed and straighten your back. Also, after sleep, you need to lie on your side, turn your head at an angle of 45 degrees.
It is worth fixing your torso in this position for 30 - 60 seconds, then sit on the bed with a straight back. You are allowed to get up only 3 – 4 minutes after performing the actions.
For the vestibular system and vision
These gymnastics exercises for the vestibular apparatus for dizziness are performed in a sitting position. The course of classes is at least 10 - 12 days.
When performing, the head should not move; all movements are carried out exclusively with the eyes.
The first exercise involves looking up, then down. The second is done by looking around. At the same time, at an intermediate distance, try to hold your gaze on some object for 5–10 seconds.
These train concentration. After this, you should perform the following exercise: move your thumb parallel to your face to a distance of about 50 - 60 centimeters. Then slowly bring it closer, concentrating your attention on it.

After such training, dizziness will appear less frequently, and if it occurs, a person will be able to quickly concentrate and protect himself from a dangerous fall.
The next complex is aimed at “training” brain structures to control the body. These activities also have a beneficial effect on the eyes.
To perform this you will need to sit down, straighten your back and place any object at a distance of 1.5 – 2 meters.
While sitting, direct your gaze to the object and fixate it. Then tilt your head, but do not take your eyes off the object.
Stand on a flat surface, spread your legs shoulder-width apart. Slowly bend down, reaching to your toes. Fix your body in this position for 1 minute. When performing, it is forbidden to bend your knees.
To correct your balance, walk backwards.
Conclusion
Vestibular gymnastics for dizziness for the elderly does not give immediate results.
To get the effect, you need to complete a whole course of training. Sometimes the first workouts make a person feel uncomfortable, but this is not scary.
This is usually an indicator of muscle stretching. After such manifestations, you should consult your doctor again.
It is likely that such an effect could appear after performing the exercises incorrectly, so after this it is better to engage in training with a physiotherapist.
Video: Vestibular gymnastics
How to train the vestibular apparatus? This organ, which regulates people’s balance, is responsible for orientation in space. A person has an apparatus in the inner ear for coordinating body movements. How to improve your balance? Special gymnastics for adults and children will help restore organ function.
The work of the vestibular apparatus
For normal human functioning, training of the vestibular apparatus is necessary. Its channels are filled with sound vibration receptors and fluid. With any movement it shimmers and causes balancing. The impulses then travel along the vestibular nerves and transmit information about the position of the body to the brain. As a result, coordination of movements occurs in those who train the organ. The vestibular apparatus sensitively perceives any changes in the position of the head and body in space. How to develop the ability to maintain balance when dizzy?
Nausea often occurs when traveling in public transport, and severe dizziness occurs. When this navigation system is disrupted, the brain receives incorrect information. A picture of the visual analyzer appears, the fluid in the vestibular apparatus moves, the eyes see movement, but the muscles are at rest. How to strengthen the vestibular apparatus? Symptoms of the pathology significantly complicate life. It is very difficult to cope with this pathology in a child.
It is important to train the vestibular system in adults after a stroke.

Strengthening exercises
From the first days of a child’s life, exercises are needed for development. You can effectively train the vestibular apparatus at home. Experts have developed special exercises for training. Systematic training of motor coordination will help adults get rid of unpleasant sensations.
Exercises for vestibular rehabilitation:
- Special shoes are used to develop the vestibular apparatus. It performs gymnastics, you can walk, run, dance.
- This unusual shoe is a vestibular apparatus trainer. When a person walks in regular shoes, he will feel much better.

Perform while standing:
- Arms are spread, legs are together. Closing your eyes, stand straight, without losing your balance, for a few seconds. Try to feel all your muscles. Then slowly lower your arms.
- Rising on your toes as high as possible, spread your arms to both sides. Try to maintain balance in this position. Then you need to be in this position for several seconds without opening your eyes. Maintain balance while standing on your toes to develop the vestibular system.
- Rise up on your toes, throw your head back as far as possible and maintain your balance in this position. Then you need to close your eyes and try to stand for a few more seconds.
- Place your hands on your waist and rise on your toes. Do several quick tilts of your head and then your torso forward. Do the same with your eyes closed.
- Raise one knee as high as possible, spread your arms to the sides. Freeze in this position for a while. Close your eyes and try to stay in this position for a little longer.
- Place one foot in front of the other in one line. The toe of the hind leg touches the heel of the front leg. Stretch your arms out to the sides and stand in this position for a while. After this, lower your arms and hold in this position for 10 seconds. Then try to stay in this pose without opening your eyes. Next, switch your legs and repeat the exercise to develop body coordination.
- The legs remain in the same position. Hands are on the belt. Alternately bend in different directions at first at low speed, trying to maintain balance. This is a good workout for the human vestibular system. You need to try to do the same with your eyes closed.
Gradually, the time spent in different poses can be increased.

Repeat head and eye movements 20 times:
- You need to move your hand with a pencil far away from you and focus your gaze on its tip. The pencil should be slowly removed and brought closer to the face, continuously fixing the gaze on the tip of the object.
- The head is completely motionless. Look high up, then slowly look down, then you need to do this at a faster pace.
- Without changing the position of your head, vigorously move your gaze left and right. At first, do these simple movements slowly, then repeat at an accelerated pace.
- Repeatedly deeply tilt your head to your chest, throw it back with your eyes open, first carefully and slowly, then with acceleration. Slowly tilt your head towards your shoulder, then faster and faster. When the dizziness stops, do this action with your eyes closed.
Therapeutic exercises in a sitting position:
- To improve the vestibular system, raise your shoulders as much as possible. Then perform vigorous rotations with your shoulders at the same time. Turn the body alternately left and right, arms bent at the elbows.
- Sitting on a chair, bend low without straining to the floor. At the same time, you need to take out a small object lying here, then return it.
- Slowly perform vestibular apparatus training, slowly rotating your head to the sides. Do 2 spins slowly first and then do 2 fast spins. When you feel better, do these exercises with your eyes closed.
- Spin around your axis with your arms extended in both directions.
Perform 20 times in a sitting or standing position:
- Get up from a sitting position. In this case, the eyes must be open.
- Repeat the exercise with your eyes closed.
For the development of the vestibular system in children, it is useful to ride on carousels. Regular sports and special exercises help strengthen your ability to coordinate movements. If you are persistent, you can train your vestibular apparatus.
The organ of balance is located in the inner ear. Its main tasks are:
- body orientation in space;
- maintaining body balance at rest and during movement.
Prolonged irritation of the vestibular apparatus can lead to disruption of its functions, which is manifested by the appearance of the symptom complex “motion sickness” (dizziness, nausea, vomiting, loss of balance, disturbances in cardiac activity and breathing rhythm). Such phenomena can occur when riding a boat or steamship, while driving a car, etc. To normalize the activity of the vestibular apparatus, training is necessary - performing a set of special exercises. Exercises should be performed daily even when the attacks of dizziness stop. Duration of classes - 15-20 minutes. When performing some exercises, patients may experience unpleasant sensations reminiscent of “seasickness,” but nevertheless they should not stop training. Over time, the load on the vestibular apparatus should gradually increase. Usually, after a few months of training, all negative phenomena disappear and health improves.
An approximate set of exercises for training the vestibular apparatus:
Starting position: legs straight, heels together, arms down.
- Tilt your head down - exhale, raise your head up - inhale.
- Turn your head left and right 10-15 times.
- Tilt the head to the left shoulder, starting position, tilt to the right shoulder 10-15 times.
- Circular movement of the head from left to right and right to left. Lowering your head - exhale, raising - inhale.
After 8-10 days of training, additional exercises should be introduced:
Starting position: arms down, legs wider than shoulders.
- Inhale. Exhaling, bend over to your left leg, reach for it with your hands, return to the starting position, and do the same for your right leg.
- Hands on the belt - inhale, turn the torso to the right - exhale, do the same to the left.
- Grasp the seat of the chair with your hands, move your torso back - inhale, return to the starting position - exhale.
Repeat each exercise 8-10 times. Exercises are done at a calm, even pace, without jerking. Breathing should be calm, through the nose. After 10 days of training, this set of exercises is performed in a standing position, feet shoulder-width apart, holding the back of a chair with your hand. After 20 days, in the absence of negative effects, you can do without the help of a chair, standing without support. Starting position: feet wider than shoulders, arms down.
At this stage of training, you can add the following exercises.
- Raise your hands up - inhale, bend forward, trying to touch the floor with your hands - exhale. Breathing is rhythmic, through the nose. The exercise is performed first with your eyes open, then with your eyes closed.
- Hands on the belt, rotating the body first to the right, then to the left, bending the body down - exhale, straightening - inhale.
- Clench your hands into fists and bend them at the elbows. Throw your right hand forward and to the left with force (the head and torso make a half-turn to the left); when the right hand returns to its original position, throw your left hand with force.
Breathing is voluntary, the exercise is performed first with eyes open, then with eyes closed. Each exercise should be performed 8-10 times.
After the exercises have been mastered, walking should be included in the set of exercises. You should walk 2 meters forward and, without turning around, walk the same amount back (walk twice). They walk first with their eyes open and then with their eyes closed. After stability is achieved, they proceed to walking with their eyes closed, both forward and backward. Gradually the number of repetitions is increased to 10 times.
To train the vestibular apparatus, various exercise machines, swings, rocking chairs, and swivel chairs are used.
Everyone needs training of the vestibular system, especially workers in such professions as pilots, astronauts, steeplejacks, sailors, etc. need it.
Remember, traditional medicine cannot completely replace the methods of classical medicine!