What to do if your child is vomiting
4Dear readers, I think everyone will agree that vomiting in children is quite common. And, without a doubt, it always indicates certain disturbances in the functioning of the body. In today's conversation with doctor Tatyana Antonyuk, we will find out what provokes this phenomenon, how to stop vomiting in children and how dangerous it can be. I give the floor to Tatyana.
Good afternoon, readers of Irina’s blog! Vomiting is not an independent disease; it is a signal about the process of intoxication of the body, the presence of illness or various malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs. There can be many reasons why it occurs. Vomiting is often accompanied by other symptoms, can be repeated and carries the risk of dehydration, but may also not be dangerous for the baby.
In most cases, it is a protective reaction of the body to a number of negative factors. When impulses arrive from the stomach, liver, and intestines, a reflex expulsion of food occurs. The period before the onset of vomiting is characteristic: the child feels nausea, his salivation increases, and his breathing quickens.
Most parents perceive vomiting as a sign of food poisoning, but it can have other causes. Vomiting in a child without fever and diarrhea occurs with the following pathologies.

Pylorospasm
These are spasmodic attacks in the stomach that occur against the background of underdevelopment of the nervous system. Usually seen in newborns and infants. In addition to profuse vomiting, the baby has restless behavior, poor sleep and insufficient weight gain. Vomiting during pylorospasm should not be confused with normal regurgitation, which occurs in all infants and is not a pathology.
Central nervous system disorders
Their main cause is disruptions caused by intrauterine developmental pathologies, fetal hypoxia, and prematurity. An attack of vomiting in this case is not associated with food intake and is accompanied by dizziness, severe weakness, and convulsions.
Intestinal obstruction
In this case, vomiting occurs against the background of severe pain and cramps in the stomach. Blood may appear in the stool. Intestinal obstruction occurs due to infection by worms, in the presence of polyps or tumors.
Entry of a foreign body into the esophagus
If the baby is not able to talk about his feelings, symptoms such as increased salivation, pain in the neck, and shortness of breath in the child will help to suspect the presence of a foreign body.
Inflammatory processes in the digestive organs
Babies may complain of nausea, heartburn, pain and bloating. You can see mucus and bile in the vomit.
Traumatic brain injuries
They often occur in infants and children of primary preschool age, since children in this category are especially active and cannot yet control their actions. If after a fall your child vomits, is agitated, or, conversely, lethargic, you should definitely consult a doctor!
Autotenic syndrome
It occurs as a result of the accumulation of large amounts of acetone in the blood. In this condition, vomiting is sudden and uncontrollable, increasing the risk of severe dehydration.
Also, vomiting in a child without fever can be one of the symptoms of increased intracranial pressure, epilepsy, migraine and other neurological disorders.

When does vomiting and diarrhea occur in a child?
Diarrhea is a symptom that often accompanies vomiting in food poisoning and some other pathological conditions. These include:
- metabolic disorders, when vomiting and diarrhea indicate lactose or gluten intolerance or may be a sign of food allergy;
- attack of appendicitis. Vomiting occurs simultaneously with severe pain in the right side and around the navel;
- food poisoning or intestinal infections. Severe vomiting with further dehydration occurs with dysentery, rotavirus, and salmonellosis. The presence of poisoning or intestinal infection is indicated by diarrhea with a foul odor, mucus and foam;
- dysbiosis. Violations of the beneficial properties develop after long-term use of antibiotics, with reduced immunity. The child is bothered by frequent diarrhea, stomach cramps, and skin rashes.
Poisoning usually occurs when eating poisonous berries or mushrooms, low-quality or expired products, or alcohol-containing substances. Vomiting and diarrhea occur when there is an overdose of medications, or when a child comes into contact with household chemicals or dangerous dyes (on toys, clothes). Nitrates and pesticides, which are generously applied to vegetables and fruits, can provoke vomiting and diarrhea. Accumulating in the body, they cause poisoning.

What is psychogenic vomiting
Children are very sensitive and emotional, so vomiting can occur as a result of fear or extreme anxiety. Some young children are prone to so-called demonstrative vomiting, when the child feels disadvantaged and lonely and thus subconsciously tries to attract the attention of adults.
In teenage girls, vomiting may be a symptom of anorexia or bulimia. With the listed violations, the child needs the help of a psychologist.
How to stop vomiting in a child at home
The first symptoms of poisoning are observed within a time period of 4-48 hours after ingestion. The child must be shown to a doctor if vomiting lasts more than a day, is aggravated by an increase in body temperature, or appears in other family members.
Vomiting that occurs always indicates a serious pathology if blood and mucus are visible in it, and the child is diagnosed with clouding of consciousness, impaired coordination of movements, and incoherent speech.
Often parents do not know what to do if their child is vomiting and begin to panic. This, of course, should not be done; you need to make sure that the child is in a position where vomit cannot enter the respiratory tract.
Babies should be turned on their side and held semi-vertically; infants should be kept in an upright position. If vomiting occurs without fever in a child, you should not rush to immediately give medications. Without a preliminary examination and identification of the cause, they can only cause harm. Also, there is no need to do gastric lavage before consulting a doctor.
If your child is poisoned and is vomiting, the most important thing to do is make sure he drinks plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. After each episode of vomiting, you need to give the child some water to rinse the mouth.
If the baby has all the signs of poisoning, but there is no vomiting, parents can induce it themselves. To do this, the child is given water or milk to drink, and then pressed with a finger or spoon on the root of the tongue. If vomiting was caused by poisoning with detergents, artificial vomiting should not be induced so that acids and alkalis do not cause burns to the mucous membranes.
In this video, Dr. Komarovsky tells what to do if the temperature rises with diarrhea and vomiting.
The use of medications is possible only after consultation with a pediatrician. The doctor prescribes the most optimal remedy and determines the dosage depending on the age and weight of the child.
Cerucal
"Cerucal" is one of the most effective remedies for vomiting and nausea in children. It is produced in the form of injection solutions or tablets, which are intended for children over 6 years of age. The child's weight must be at least 20 kg. The usual dosage of Cerucal tablets for children with vomiting is 0.5-1 tablet three times a day.
The drug is taken 30 minutes before meals, washed down with plenty of liquid. Children under 6 years of age or those who weigh less than 20 kg are prescribed the medicine in the form of injections. Contraindications include kidney pathologies.
Motilium
The drug is available in tablets or a sweet suspension, which is prescribed to children under 5 years of age. The active substance of the drug is domperidone. It blocks the vomiting center of the central nervous system, stimulates the passage of food into the stomach, and prevents the development of congestion in the intestines.
The drug is approved for use by newborns with excessive regurgitation and cyclic vomiting. However, during treatment, the small patient must be under the supervision of a doctor.
According to the Motilium instructions, for children with vomiting, the dosage is 0.25-0.5 ml per kilogram of the child’s weight. The drug is taken 3-4 times a day half an hour before meals. Contraindications: intestinal obstruction and gastric bleeding. The drug is prescribed with caution to children with neurological problems.
Smecta
The drug belongs to the group of sorbents. The therapeutic effect of “Smecta” for vomiting in children is as follows: the active substance creates a protective film, preventing the absorption and spread of toxins and bacteria. The product is not absorbed into the blood, so it is absolutely safe even for newborns.
The drug is produced in the form of sachets, the contents of which must be diluted in tea, water or infant formula. Duration of treatment – from 3 to 7 days.
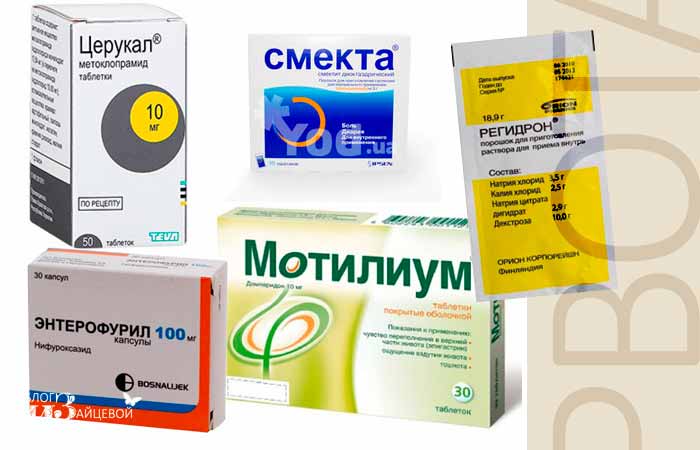
Regidron
High fever and vomiting in a child cause severe dehydration. This can be dangerous not only for the health, but also for the life of the baby. "Regidron" for children with vomiting is prescribed to normalize the water and acid-base balance.
The release form of the drug is powder in sachets, which is diluted in water. When using the drug, it is important to follow the recommended dosages, starting with small doses. Contraindications for use: diabetes mellitus, renal failure.
Enterofuril
The antimicrobial drug has proven itself in the fight against food poisoning. "Enterofuril" for vomiting in a child without diarrhea gives an effective result, is not absorbed in the intestines, and activates the immune system. The release form for children is a suspension with a pleasant aroma. Children over 3 years old can be prescribed the drug in tablet form.
"Enterofuril" is taken regardless of meals. It is not recommended for simultaneous use with sorbents. Side effects are very rare.
We invite you to watch a video in which Polina Dudchenko, family doctor, neonatologist, and lactation consultant, shares recommendations regarding situations where a child is vomiting.
The concern of parents who want to know what to feed their child after vomiting is understandable. During this period, you need to follow certain nutritional principles:
- do not force feed the child;
- drink plenty of fluids to reduce the risk of dehydration;
- introduce into the menu products that have a gentle effect on the digestive system;
- the first dishes after vomiting should be liquid dietary porridge made from rice, buckwheat or oatmeal;
- When choosing products, take into account the reasons that caused vomiting.
Breastfeeding does not stop during vomiting, but previously introduced complementary foods must be stopped until complete recovery.
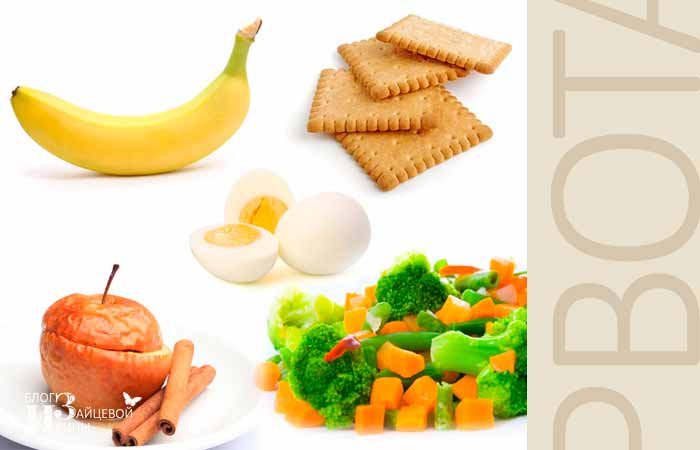

What to feed a child after vomiting in the first days?
In addition to cereals, these can be:
- in the form of puree;
- boiled carrots and broccoli;
- homemade crackers or biscuits;
- bananas;
- boiled eggs;
- vegetarian vegetable soups;
- fruit jelly with starch.
Fish and meat dishes are canceled in the first 3-4 days of illness. If you are feeling well, they can be included in the menu in the form of steam cutlets or meatballs. Meals should be small, every three to four hours. During the week, all meals should be low-fat and dietary.
What not to feed a child who is vomiting
From the diet you need to completely exclude fatty and smoked foods, sausages, milk, fresh baked goods, sweets, mushrooms, strong meat broths, fast food, various sauces and mayonnaise. If vomiting is complicated by diarrhea, you should not give fermented milk products, legumes, beets, or prunes. As for drinks, store-bought juices from packages, sweet carbonated water, strong black tea, etc. are prohibited.
A proper diet after vomiting is an important component of the comprehensive treatment of children. Its strict adherence will save the baby from vomiting and help avoid negative consequences.
In the future, you need to be very careful when choosing products that are included in the baby’s menu, and teach the child the rules of general hygiene.
Your doctor
Tatiana Antonyuk
I thank Tatyana for highlighting this important issue for many parents. Vomiting in children is always a cause for concern, and, of course, you need to understand when this condition does not threaten the child with anything, and you only need time and certain measures to cope with it, and when you need to urgently consult a doctor.
Consequences of gallbladder removal. Postcholecystectomy syndrome