How to transfer an image to paper. Methods for transferring an image from paper to wood
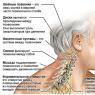
Vocal cords are paired muscular-fibrous formations that perform the function of human voice production. Before analyzing the pathology of the ligaments, it is worth understanding the anatomy of the larynx - the organ that houses these structures.
The larynx is a hollow organ that is an element of the human respiratory system. The most important function is also voice production. Above, the larynx connects with the lower part of the pharynx, and below it passes into the trachea.
Anatomical structure
The base of the larynx is made up of hyaline cartilage. They are connected to each other using joints and ligaments. The larynx contains small (paired) and large unpaired cartilages: epiglottis, thyroid and cricoid cartilage (the last two can be palpated through the skin).
Inside, the larynx is lined with a mucous membrane that performs protective, nutritional and other functions.
On the outside, the cartilaginous skeleton is covered with muscles and fiber, separating the organ from neighboring formations.
Laryngeal folds
Between the cartilages of the larynx there are two pairs of folds of the mucous membrane of the organ: vocal and vestibular.
The vestibule (false) folds also contain muscle elements, but they are not sufficiently developed. Therefore, these formations do not participate in the process of voice formation.
Voice production mechanism
Sound is created in the following way: under voluntary human effort, the width of the glottis and the degree of tension of the vocal cords change during passage air flow through the larynx. The resistance to the flow of the folds is what creates the vocal sound.
Causes of pain in the vocal cords
In most cases, the cause of pain in the vocal area of the larynx is an inflammatory process - laryngitis, which occurs as a cold due to hypothermia. However, pathology of the vocal cords can be caused by other serious reasons:
- Diphtheria.
- False croup.
- Tumors of the larynx.
- Foreign bodies.
Some factors affect ligaments quite rarely, but their impact is quite possible. Rare causes of vocal cord pain include:
- Injuries.
- Inhalation exposure to toxic substances.
- Laryngeal polyps.
- Tuberculosis.
Diagnosis of diseases of the larynx
If a person continues to have symptoms of damage to the larynx and vocal cords for a long time, and treatment at home does not help, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will conduct the necessary tests. Diagnostic methods include:
- Examination of the throat using a spatula - pharyngoscopy.
- External palpation of the neck organs.
- Laryngoscopy is an examination of the larynx using a special device, a laryngoscope.
- X-ray and other radiation techniques.
- Biopsy is the removal of material for microscopic examination.
Acute laryngitis is an inflammatory disease of the larynx and vocal cords that occurs under the influence of bacteria and viruses. Symptoms of laryngitis
- Feeling of pain, soreness, discomfort in the throat.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Cough, often dry.
- Increased body temperature (optional sign).
Causes of laryngitis
The inflammatory process most often develops after hypothermia, overstrain of the vocal cords, smoking and drinking alcohol, or inhaling air contaminated with dust or gas. The larynx activates its own microflora, to which the body is resistant under normal conditions. Another causative agent of laryngitis may be a virus (for example, influenza or measles).
Laryngitis can be caused by an allergic reaction due to inhalation of irritants, insect bites, or consumption of allergens.
Treatment of laryngitis
What to do if the larynx is inflamed? To relieve symptoms in early period treatment, it is recommended to create peace for the vocal folds: stop smoking, strain the ligaments, avoid spicy and cold foods.
A gentle regime for the whole body is indicated: rest, warmth, abundant alkaline drinking.
For laryngitis, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of spray and inhalation. Sometimes antibiotics are indicated in the same dosage forms.
Within two weeks, with proper therapy, the symptoms of the disease cease to bother the patient.
Chronic laryngitis
With improper treatment of acute laryngitis, concomitant smoking, professional overstrain of the vocal cords, harmful dust and gas factors in production, there is a high risk of developing chronic laryngitis.
The symptoms of the disease repeat the acute form of the pathology. Chronic laryngitis worsens several times a year and causes significant inconvenience to the patient.
Treatment of chronic laryngitis
Therapy for the disease is complex and often has low results.
Inhalations using oil and alkaline solutions show good results. It is recommended to use a nebulizer - a device that sprays a substance in the form of tiny droplets.
Treatment for exacerbation of the disease is identical to the treatment of acute laryngitis.
When areas of mucosal hyperplasia - cell proliferation - form on the larynx, their surgical removal is necessary. Patients with this pathology are registered at the dispensary to prevent the development of laryngeal cancer.
Diphtheria is a disease that develops more often in children, caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae. This disease is manifested by the formation of croup in the throat - inflammation with the formation of films on the vocal folds, which interfere with breathing and voice production.
The so-called false croup is formed under the influence viral infection and not only amazes vocal cords, but also other parts of the larynx.
Symptoms of croup
The most striking manifestation of croup, both with diphtheria and with a viral infection, is a loud “barking” cough. This symptom is formed due to difficulty in passing air through the larynx narrowed by the film. Other signs are:
- Wheezing when breathing.
- A bluish tint to the skin is cyanosis.
- Increased body temperature.
- Difficulty and increased breathing rate.
Treatment
Depending on the cause of the pathology, croup is treated in various ways. Inhalation of humidified air and steam have a good effect. For diphtheria, antibiotics are added to this treatment, which are used in various forms, including inhalation.
In severe cases of pathology, inhalation of corticosteroids is used - hormonal drugs that effectively relieve inflammation in the larynx.
False croup caused by viruses is not effectively treated with antibiotics. Use drugs that stimulate the immune system, the above inhalations. For croup in children, hospitalization is necessary to prevent the development of laryngeal stenosis - obstruction of the organ with the inability to breathe.
Symptoms
Signs of a tumor include prolonged sore throat, hoarseness, dry cough, difficulty breathing and swallowing. Later, symptoms of general weakness, weight loss, and susceptibility to frequent colds appear.
Treatment of tumors
Treatment is exclusively surgical. If a tumor is detected in a timely manner, surgical intervention leads to good results treatment, and modern rehabilitation techniques make it possible to maintain the quality of life of patients.
Foreign bodies
What to do in this case? Be sure to consult a doctor. Foreign bodies are removed using a bronchoscope, which is inserted into the larynx. The doctor, under the control of his own vision, can easily detect and remove an object from the larynx.
Pharynx- this is a canal with muscular walls that connects the mouth and nasal sinuses with the larynx and esophagus; The pharynx is also an organ of the digestive system. Larynx- a canal with cartilaginous walls connecting the pharynx to the trachea; Air passes through the larynx into and out of the lungs, and this organ also serves as a voice resonator.
This is a funnel-shaped channel from 12 to 14 cm long and 35 mm wide at the upper edge and 15 mm at the lower edge. The pharynx is located behind the sinuses and oral cavity, it deepens into the neck and then passes into the larynx and esophagus. It is an integral part of both the respiratory system and the digestive system: the air we breathe, as well as food, passes through the pharynx.
There are three segments in the pharynx: the upper pharynx, or nasopharynx, connected by its anterior wall with the nasal sinuses, on the upper wall of which there is a formation of lymphatic tissue called the pharyngeal tonsil; the middle pharynx, or oropharynx, which communicates with the upper part of the oral cavity and on the side walls has formations of lymphatic tissue called palatine tonsils; and the lower part of the pharynx, or laryngopharyngeal space, which is connected in front to the larynx and behind to the esophagus.

The dual function that the pharynx performs is possible thanks to the epiglottis - a tennis racket-shaped formation located on the upper wall of the larynx; Normally, the epiglottis remains open, allowing air to pass from the larynx to the nose and vice versa, however, during swallowing, the epiglottis closes and blocks the entrance to the larynx - this forces the bolus of food towards the esophagus.
It is a truncated cone-shaped canal consisting of many articular cartilages connected by various muscles, membranes and ligaments. The larynx is located between the pharynx and trachea, its size changes with age: in an adult, the larynx reaches 3.5-4.5 cm in length, 4 cm in the transverse section and 2.5-3.5 cm in the anteroposterior section.
At the top of the larynx is the epiglottis, a cartilage whose movements direct air into the trachea during breathing and limit its flow during swallowing. In addition to supplying air to the lungs and removing it, the larynx performs no less than important function: forms sounds human voice. On the inner surface of the larynx on each side there are two folds: fibrous - false vocal cords and fibromuscular - true vocal cords, separated from each other by a V-shaped gap called the glottis, which is responsible for the formation of sounds (more details about the structures larynx can be read in the following articles: muscles of the larynx, cartilages and joints of the larynx, laryngeal cavity, vocal folds of the larynx and functions of the larynx).

From the ligamentous apparatus of the larynx, it is worth remembering the following: the larynx is attached to the hyoid bone on the thyrohyoid membrane, and between the arch of the cricoid and the lower edge of the thyroid cartilage is stretched a strong elastic cricothyroid ligament.
Small ligaments strengthen both joints of the larynx and fix the epiglottis to the hyoid bone and the angle of the thyroid cartilage. The most famous is the vocal cord; it is located between the thyroid cartilage and the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage of the corresponding side. Parallel to it and slightly higher runs a not sharply defined vestibular fold. They are both paired.
The vocal cords form the glottis. How the voice changes depends on its width and the degree of tension of the ligaments themselves. Both are determined by the contraction of one or another striated muscle. Therefore, having examined the cartilaginous, articular and ligamentous apparatus, it is logical to pay attention to the muscles of the larynx. To understand the principle underlying the movement of the larynx.
The sounds a person makes arise from the vibration of the vocal cords as air passes from the lungs back into the lungs. oral cavity; Man forms words from sounds. When inhaling, as when exhaling, when a person is not speaking, his vocal cords are relaxed and lean against the walls of the larynx so that the air passes without any resistance. Conversely, when a person speaks, during exhalation, thanks to the muscles that contract the laryngeal cartilages, the vocal cords tense, approach the midline of the larynx and vibrate before the air from the lungs is released. Thus, according to the degree of tension and the shape that the vocal cords take at a certain moment, sounds of different pitches are formed.
Very often we are faced with the question - how to transfer a drawing to paper? The question is very important, because everything depends on the quality of the translated image. further work. You found a wonderful drawing in a book or magazine, or maybe you have a beautiful embroidery in front of you that you want to repeat - the topic of transferring a drawing to paper is for you!
The task before us is to transfer a clear, neat drawing from a sample drawing onto paper, which will then be transferred to another surface: fabric, leather, cardboard, paper, wood or plywood. In some cases, this drawing itself will be the basis for work, for example, as a coloring book for children.
Let's look at several options for transferring a drawing to paper.
OPTION 1.
Let's start with the most interesting and quite old method, which has been used in their work for several generations of masters. He enjoyed particular respect among students, in whose time the technology for printing drawings and texts was not yet so accessible. Lots of neat coursework and theses went through GLASSING and were successfully defended.

In order for you to be able to transfer any drawing onto paper using glass, you need a table lamp, two chairs and glass of any size. That's all - you now have reliable manual copying “equipment” at home under your leadership! Let's look at what to do now and how to transfer the drawing onto paper using glass.
We place a sample on the glass (approximately above the lamp) from which we will copy the drawing.

Put it on this sample blank slate paper.


Enough bright light table lamp allows you to clearly see the pattern through all layers of paper. Take a pencil and trace all the lines of the bottom drawing onto the top blank sheet of paper.
If you do not want the bottom sheet to be damaged by pencil pressure, then trace the lines with light pressure. Then, turning off the lamp, take a pencil and trace the lines more clearly.

The work is completed, the patterns are translated into new leaf paper. In this way, you can copy drawings not only from a simple sheet, but also from any book and magazine.

Glazing is a wonderful way to transfer a pattern onto paper!
Interestingly, the bright light of the lamp also penetrates the fabric, so you can copy the pattern from embroidered products. This is done in the same way as when working with paper.

The napkin lies on the glass above the lamp. A blank sheet of paper is placed on top and the entire pattern is outlined with a pencil. Keep in mind that the embroidery is slightly convex and the top blank sheet of paper will not lie tightly on the napkin.

Drawings translated using the glass method are distinguished by their accuracy. You can start working periodically, giving yourself time to rest, because the drawing lies in place without moving. This method is good for any drawings of any complexity.
OPTION 2.
If the drawing is small in size, it can be transferred to paper on a regular WINDOW GLASS . Besides, There are times when there is no opportunity or space to make a structure with glass, chairs and a lamp.

To prevent the bottom sample from moving, secure it to a blank sheet of paper using paper clips. A significant drawback when working - very quickly hands get tired.
OPTION 3.
Usage COPY PAPER for drawing translation is widely known. To work you need: a sample drawing, carbon copy, blank paper, pencil or pen.
All this is laid out in this way - first a blank sheet, then a carbon copy with the ink side down, a sample of the design is placed on top. Staples are needed to ensure that nothing moves while working.
With a pencil, with pressure, all the lines of the drawing are outlined, which remain on the bottom sheet of paper.

After finishing the work, remove the carbon paper - the drawing is completely imprinted on a sheet of paper.

There are several disadvantages of transferring a drawing using carbon paper - the sample quickly wears out due to frequent tracing with a pencil, the work is sloppy, this method is suitable for relatively small drawings.
OPTION 4.
In some cases, you can transfer the drawing directly onto thin tissue paper. paper or thicker tracing paper.

This translucent paper is superimposed on a sample drawing, the contours of which are outlined using a pencil or pen.

That's it. A lot has been written, but you need to know each of these options for transferring a drawing onto paper. The work of needlewomen is quite varied - you don’t know when what knowledge will come in handy.
Let's summarize our " manual" methods of drawing translation. So this is:
- glass above the table lamp,
- glass on the window,
- using carbon paper,
- using tracing paper or tissue paper.
But!.. Modernity makes its own adjustments to the work of craftsmen. Required drawing If desired, you can already find it on the Internet. And the pattern you like can bescan and into electronic form print on a printer.As a result, you will have a drawing on paper ready to work.Due to the fact that there is no manual drawing, time is saved significantly and after printing you can start working directly.
If you have a photocopier nearby, you can take a sample drawing on it, increasing or decreasing its size if necessary. The person servicing this device knows its additional functions. Just tell me by what percentage you would like to change the image.
So, modern way The translation of the drawing is as follows:
- scan images from books and magazines and print,
- find the finished picture in electronic form and print it,
- use a photocopier for copying, print and changing the size of the picture.
Copying and printing of drawings of any format and color is carried out on modern technology in a matter of minutes. The print quality is excellent.
But think about it, if many masters still with a simple pencil transfer the drawings onto paper themselves, then this manual method is not so bad... Time-tested!
Thank you and see you again on the pages!