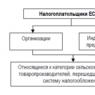
Allied and non-union subordinating relationship in a complex sentence. Complex sentences with different types of connection
The subordinating relationship in a complex sentence has several types. By the presence or absence of an analogy with the types of subordinating connection in a phrase and a simple sentence, there is reason to distinguish two types of subordinating connection in complex sentences: 1) a connection similar to connections in a phrase and a simple sentence; 2) a connection that is not similar to connections in a phrase and a simple sentence.
The subordinating relationship of the first kind is further subdivided according to what kind of relationship it is analogous to. For a subordinating connection in a complex sentence, the most significant feature is predictability ~ unpredictability. Accordingly, they stand out:
- a predictive subordinating connection, similar to the connection between a word and the form of the word that spreads it, determined by the properties of the main word;
- non-predictive subordinating connection, similar to the connection between the predicative center of the sentence and its non-constitutive situational distributors - determinants. Wed: He was waiting for the director to come. - When the director arrived, they went to the workshop. In the first sentence, the subordinate clause is in a subordinate relationship with the word wait, the categorical properties of which explain both its very presence with this word and the nature of its design; in the second sentence, the subordinate part is in a subordinate relationship with the predicative center of the main part, and the very fact of the presence of the subordinate part and the nature of its design (not motivated by anything in the main part) are determined by the semantic relations that are established between the subordinate and main parts.
More on the topic § 74. TYPES OF SUBJECTIVE COMMUNICATION IN A COMPLEX SENTENCE:
- A9. Offer. Types of sentences by the number of grammatical foundations. Types of complex sentences by means of communication of parts. Complex sentences with different types of connection.
- TYPES OF SUBJECTIVE COMMUNICATION AT THE LEVEL OF TERMS AND SIMPLE SENTENCES
- 28. Complex sentence. Means and ways of expressing relations between parts of a complex sentence. Composing, subordinating and non-union communication.
- SUBJECTIVE ALLIANCES INSIDE A SIMPLE SENTENCE
- Varieties of subordination in the phrase: coordination, control, adjoining, their characteristics, types, difficult cases.
- § 11. Sentences with a combination of non-union, coordinating and subordinating connection of predicative links.
- COMPOUND SENTENCES WITH SUBJECTIVE CONNECTIONS AND RELATIVE WORDS
- According to the sections "Subordinate relations of words and phrases", "Simple sentence", "Syntax of the word form"
- Compound sentence as a unit of syntax. The place of a complex sentence in the syntactic system. Structural and semantic features of a complex sentence.
- Principles of classification of compound sentences. Structural and semantic characteristics of the types of compound sentences. The place of complex sentences with connecting and gradational unions in the system of a complex sentence. Question about compound sentences with explanatory conjunctions.
Complex sentences with different types of connection- This complex sentences , which consist of at least of three simple sentences , interconnected by a coordinating, subordinating and non-union connection.
To understand the meaning of such complex structures, it is important to understand how the simple sentences included in them are grouped together.
Often complex sentences with different types of connection are divided into two or more parts (blocks), connected with the help of coordinating unions or union-free; and each part in structure is either a complex sentence or a simple one.
For example:
1) [Sad I]: [No friend with me], (with whom I would wash down a long parting), (to whom I could shake hands from the heart and wish many merry years)(A. Pushkin).
This is a complex sentence with different types of connection: non-union and subordinating, it consists of two parts (blocks) that are non-unionly connected; the second part reveals the reason for what is said in the first; The first part of the structure is a simple sentence; Part II is a complex sentence with two subordinate clauses, with homogeneous subordination.
2) [lane was all in the gardens], and [the fences grew lindens throwing now, by the moon, a wide shadow], (so that fences And gates on one side completely drowned in darkness)(A. Chekhov).
This is a complex sentence with different types of communication: coordinating and subordinating, consists of two parts connected by a coordinating connecting union and, the relations between the parts are enumerative; The first part of the structure is a simple sentence; Part II - a complex sentence with a subordinate clause; the subordinate clause depends on everything main, joins it with a union so.
In a complex sentence, there may be sentences with various types of allied and allied connection.
These include:
1) composition and submission.
For example: The sun set, and night followed day without interval, as is usually the case in the south.(Lermontov).
(And - a coordinating union, as - a subordinating union.)
Schematic of this offer:

2) composition and non-union communication.
For example: The sun had long since set, but the forest had not yet had time to subside: the doves murmured near, the cuckoo cuckooed in the distance.(Bunin).
(But - a coordinating conjunction.)
Schematic of this offer:

3) subordination and non-union communication.
For example: When he awoke, the sun was already rising; the barrow obscured him(Chekhov).
(When - subordinating union.)
Schematic of this offer:

4) composition, subordination and non-union connection.
For example: The garden was spacious and grew only oaks; they had only recently begun to blossom, so that now through the young leaves one could see the whole garden with its stage, tables and swings.
(And is a coordinating conjunction, so a subordinating conjunction.)
Schematic of this offer:
In complex sentences with a coordinating and subordinating connection, coordinating and subordinating unions may be nearby.
For example: The weather was fine all day, but when we sailed to Odessa, it began to rain heavily.
(But - a coordinating union, when - a subordinating union.)
Schematic of this offer:

Punctuation marks in sentences with different types of connection
In order to correctly punctuate complex sentences with different types of connection, it is necessary to single out simple sentences, determine the type of connection between them and select the appropriate punctuation mark.
As a rule, a comma is placed between simple sentences as part of a complex one with different types of connection.
For example: [In the morning, in the sun, the trees were covered with luxurious hoarfrost] , and [this went on for two hours] , [then the frost disappears] , [sun closed] , and [the day passed quietly, thoughtfully , with a drop in the middle of the day and anomalous lunar twilight in the evening].
Sometimes two, three or more simple offers most closely related to each other in meaning and can be separated from other parts of a complex sentence semicolon . Most often, a semicolon occurs in place of an allied connection.
For example: (When he woke up) [the sun was already rising] ; [the barrow obscured him].(The proposal is complex, with different types of connection: with allied and allied connection.)
In the place of an allied bond between simple sentences in complex possible Also comma , dash And colon , which are placed according to the rules for punctuation in a non-union complex sentence.
For example: [The sun has long since set] , But[the forest hasn't died down yet] : [doves murmured near] , [Cuckoo calls in the distance]. (The proposal is complex, with different types of connection: with allied and allied connection.)
[Leo Tolstoy saw a broken burdock] – and [lightning flashes] : [there was an idea for an amazing story about Hadji Murad](Paust.). (The sentence is complex, with different types of connection: coordinative and non-union.)
In complex syntactic constructions that break up into large logical-syntactic blocks, which themselves are complex sentences or in which one of the blocks turns out to be a complex sentence, punctuation marks are placed at the junction of the blocks indicating the relationship of the blocks, while maintaining the internal signs placed on their own. own syntactic basis.
For example: [Bushes, trees, even stumps are so familiar to me here], (that wild clearing has become like a garden to me) : [every bush, every pine, fir-tree caressed], and [they all became mine], and [it's like I planted them], [this is my own garden](Prishv.) - at the junction of blocks there is a colon; [Yesterday a woodcock stuck its nose into this foliage] (to get a worm out from under it) ; [at this time we approached], and [he was forced to take off without throwing off the worn layer of old aspen leaves from his beak](Shv.) - at the junction of blocks there is a semicolon.
Particularly difficult is punctuation at the junction of the writing And subordinating unions (or a coordinating union and an allied word). Their punctuation is subject to the laws of the design of sentences with a coordinating, subordinating and non-union connection. However, at the same time, proposals in which several unions are nearby stand out and require special attention.
In such cases, a comma is placed between unions if the second part of the double union does not follow. then yes, but(in this case, the subordinate clause can be omitted). In other cases, a comma is not placed between the two unions.
For example: Winter was coming and , when the first frosts hit, it became hard to live in the forest. - Winter was approaching, and when the first frosts hit, it became hard to live in the forest.
You can call me but , If you don't call today, we'll leave tomorrow. You can call me, but if you don't call today, we'll leave tomorrow.
I think that , if you try hard, you will succeed. “I think that if you try hard, you will succeed.
Syntactic analysis of a complex sentence with different types of connection
Scheme for parsing a complex sentence with different types of communication
1. Determine the type of sentence according to the purpose of the statement (narrative, interrogative, incentive).
2. Indicate the type of sentence by emotional coloring (exclamatory or non-exclamatory).
3. Determine (by grammatical foundations) the number of simple sentences, find their boundaries.
4. Determine the semantic parts (blocks) and the type of connection between them (union-free or coordinative).
5. Give a description of each part (block) in terms of structure (simple or complex sentence).
6. Draw up a proposal scheme.
A SAMPLE OF ANALYZING A COMPLEX OFFER WITH DIFFERENT TYPES OF CONNECTION
[Suddenly a thick fog], [as if separated by a wall He me from the rest of the world], and, (so as not to get lost), [ I decided
As noted above, a subordinating relationship is commonly understood as an asymmetric relationship between the parts of a complex sentence, when one sentence depends on the other and is an integral part of it. The first sentence is usually called the main one, the second - the subordinate one.
Parts of a complex sentence with a subordinating relationship can be connected in both an allied and non-union way.
In the case when parts of a complex sentence are connected in a non-union way, inversion is usually used, which indicates the subordination of one sentence to another.
With the allied method of connecting parts of a complex sentence, the following connecting links are used:
Conjunctions can consist of one word (that, because, though, etc.), several (in order that, providing that, for al that, so far as, etc.) or be paired (as.. .as, such...as, etc.). Some conjunctions can be used in combination with particles (even if, even though, even when, just as, etc.)
There are several types of subordinating relationship in English. These include the following: subject, predicative, additional, circumstantial (time, place and direction, causes, goals, conditions, concessions, consequences, comparisons), attributive, appositive. Let's give examples.
1. Subject clauses
For example:
That you may meet him at his party is quite possible.
What I need now is someone to do the job.
2. Predicative clauses
For example:
His only desire was that his family shouldn't interefere with his plans.
The question was why no one had heard the shot.
3. Offers with additional connection (object clauses)
For example:
I thought (that) they were joking
We were sorry (that) we had missed Father by a few minutes.
- 4. Adverbial clauses
- a) time (of time)
For example:
When they reached the village, Jane got out of the taxi and looked about her
b) places and directions (of place and direction)
For example:
They stopped where the road turned to the river
c) reasons (of cause)
For example:
He was glad to talk to her because it set her at ease.
d) goals (of purpose)
For example:
He spoke loudly and clearly so that all could hear him.
e) conditions (of condition)
For example:
If we start off now, we'll arrive there by dinner time.
f) concessions (of concession)
For example:
Although it was very late, she kept the dinner warm on the stove.
g) consequences (of consequence)
For example:
He was so embarrassed that he could hardly understand her.
h) comparisons (of comparison)
For example:
He now took better care of his old father than he had ever done it before.
1. Attributive clauses
For example:
I know a man who can help us.
6. Attributive clauses
For example:
I had the impression that she was badly ill.
Despite the fact that the subordination involves the subordination of one sentence to another, a complex sentence can consist of two or more sentences. In this case, it can form a whole hierarchy of sentences with various types of subordination.
For example:
I see
The structure of this proposal can be represented as follows:
A complex sentence can have several subordinating sentences, interconnected by various types of subordinating relationship. Consider the following sentence:
All she was saw that she might go to prison for a robbery she had committed years ago.
The connection of subordinating sentences and their relationship to the main one can be represented using the following scheme:
This scheme of a complex sentence gives us the opportunity to clearly represent the relationship between the main clause and the subordinate ones.
Thus, summing up the above, it is worth noting that a compound and a complex sentence are complex syntactic structures that can include more than two sentences and detect different types of syntactic links between them.
Complex sentences with different types of connection- This complex sentences , which consist of at least of three simple sentences , interconnected by a coordinating, subordinating and non-union connection.
To understand the meaning of such complex structures, it is important to understand how the simple sentences included in them are grouped together.
Often complex sentences with different types of connection are divided into two or more parts (blocks), connected with the help of coordinating unions or union-free; and each part in structure is either a complex sentence or a simple one.
For example:
1) [Sad I]: [No friend with me], (with whom I would wash down a long parting), (to whom I could shake hands from the heart and wish many merry years)(A. Pushkin).
This is a complex sentence with different types of connection: non-union and subordinating, it consists of two parts (blocks) that are non-unionly connected; the second part reveals the reason for what is said in the first; The first part of the structure is a simple sentence; Part II is a complex sentence with two subordinate clauses, with homogeneous subordination.
2) [lane was all in the gardens], and [the fences grew lindens throwing now, by the moon, a wide shadow], (so that fences And gates on one side completely drowned in darkness)(A. Chekhov).
This is a complex sentence with different types of communication: coordinating and subordinating, consists of two parts connected by a coordinating connecting union and, the relations between the parts are enumerative; The first part of the structure is a simple sentence; Part II - a complex sentence with a subordinate clause; the subordinate clause depends on everything main, joins it with a union so.
In a complex sentence, there may be sentences with various types of allied and allied connection.
These include:
1) composition and submission.
For example: The sun set, and night followed day without interval, as is usually the case in the south.(Lermontov).
(And - a coordinating union, as - a subordinating union.)
Schematic of this offer:

2) composition and non-union communication.
For example: The sun had long since set, but the forest had not yet had time to subside: the doves murmured near, the cuckoo cuckooed in the distance.(Bunin).
(But - a coordinating conjunction.)
Schematic of this offer:

3) subordination and non-union communication.
For example: When he awoke, the sun was already rising; the barrow obscured him(Chekhov).
(When - subordinating union.)
Schematic of this offer:

4) composition, subordination and non-union connection.
For example: The garden was spacious and grew only oaks; they had only recently begun to blossom, so that now through the young leaves one could see the whole garden with its stage, tables and swings.
(And is a coordinating conjunction, so a subordinating conjunction.)
Schematic of this offer:
In complex sentences with a coordinating and subordinating connection, coordinating and subordinating unions may be nearby.
For example: The weather was fine all day, but when we sailed to Odessa, it began to rain heavily.
(But - a coordinating union, when - a subordinating union.)
Schematic of this offer:

Punctuation marks in sentences with different types of connection
In order to correctly punctuate complex sentences with different types of connection, it is necessary to single out simple sentences, determine the type of connection between them and select the appropriate punctuation mark.
As a rule, a comma is placed between simple sentences as part of a complex one with different types of connection.
For example: [In the morning, in the sun, the trees were covered with luxurious hoarfrost] , and [this went on for two hours] , [then the frost disappears] , [sun closed] , and [the day passed quietly, thoughtfully , with a drop in the middle of the day and anomalous lunar twilight in the evening].
Sometimes two, three or more simple offers most closely related to each other in meaning and can be separated from other parts of a complex sentence semicolon . Most often, a semicolon occurs in place of an allied connection.
For example: (When he woke up) [the sun was already rising] ; [the barrow obscured him].(The proposal is complex, with different types of connection: with allied and allied connection.)
In the place of an allied bond between simple sentences in complex possible Also comma , dash And colon , which are placed according to the rules for punctuation in a non-union complex sentence.
For example: [The sun has long since set] , But[the forest hasn't died down yet] : [doves murmured near] , [Cuckoo calls in the distance]. (The proposal is complex, with different types of connection: with allied and allied connection.)
[Leo Tolstoy saw a broken burdock] – and [lightning flashes] : [there was an idea for an amazing story about Hadji Murad](Paust.). (The sentence is complex, with different types of connection: coordinative and non-union.)
In complex syntactic constructions that break up into large logical-syntactic blocks, which themselves are complex sentences or in which one of the blocks turns out to be a complex sentence, punctuation marks are placed at the junction of the blocks indicating the relationship of the blocks, while maintaining the internal signs placed on their own. own syntactic basis.
For example: [Bushes, trees, even stumps are so familiar to me here], (that wild clearing has become like a garden to me) : [every bush, every pine, fir-tree caressed], and [they all became mine], and [it's like I planted them], [this is my own garden](Prishv.) - at the junction of blocks there is a colon; [Yesterday a woodcock stuck its nose into this foliage] (to get a worm out from under it) ; [at this time we approached], and [he was forced to take off without throwing off the worn layer of old aspen leaves from his beak](Shv.) - at the junction of blocks there is a semicolon.
Particularly difficult is punctuation at the junction of the writing And subordinating unions (or a coordinating union and an allied word). Their punctuation is subject to the laws of the design of sentences with a coordinating, subordinating and non-union connection. However, at the same time, proposals in which several unions are nearby stand out and require special attention.
In such cases, a comma is placed between unions if the second part of the double union does not follow. then yes, but(in this case, the subordinate clause can be omitted). In other cases, a comma is not placed between the two unions.
For example: Winter was coming and , when the first frosts hit, it became hard to live in the forest. - Winter was approaching, and when the first frosts hit, it became hard to live in the forest.
You can call me but , If you don't call today, we'll leave tomorrow. You can call me, but if you don't call today, we'll leave tomorrow.
I think that , if you try hard, you will succeed. “I think that if you try hard, you will succeed.
Syntactic analysis of a complex sentence with different types of connection
Scheme for parsing a complex sentence with different types of communication
1. Determine the type of sentence according to the purpose of the statement (narrative, interrogative, incentive).
2. Indicate the type of sentence by emotional coloring (exclamatory or non-exclamatory).
3. Determine (by grammatical foundations) the number of simple sentences, find their boundaries.
4. Determine the semantic parts (blocks) and the type of connection between them (union-free or coordinative).
5. Give a description of each part (block) in terms of structure (simple or complex sentence).
6. Draw up a proposal scheme.
A SAMPLE OF ANALYZING A COMPLEX OFFER WITH DIFFERENT TYPES OF CONNECTION
[Suddenly a thick fog], [as if separated by a wall He me from the rest of the world], and, (so as not to get lost), [ I decided
Phrase.
With the help of the site, you can easily learn how to determine the type of subordinating relationship.
subordination- this is a connection that unites sentences or words, one of which is the main (subordinate), and the other is dependent (subordinate).
phrase- this is a combination of two or more significant words related to each other in meaning and grammatically.
green eyes, writing letters, hard to convey.
In the phrase, the main (from which the question is asked) and the dependent (to which the question is asked) word is distinguished:
Blue ball. Rest outside the city. The ball and rest are the main words.
Trap!
The following are not subordinating phrases:
1. The combination of an independent word with a service: near the house, before a thunderstorm, let him sing;
2. Combinations of words as part of phraseological units: beatbuckets, fool around, headlong;
3. Subject and predicate: night has come;
4. Compound word forms : lighter, will walk;
5. Groups of words united by a coordinating link: Fathers and Sons.
Video about types of subordination
If you like the video format, you can watch it.
There are three types of subordination:
| connection type | What part of speech can the dependent word be? | what question is asked to the dependent word |
| agreement (when the main word changes, the dependent word changes): seashore, young people reading, first snow, my home |
adjective, participle, ordinal number, some categories of pronouns | Which? Questions may vary by case! |
| control (when changing the main word, the dependent does not change): | noun or pronoun in the indirect case with or without a preposition | questions of indirect cases (of whom? what? - about whom? about what?) Remember! The prepositional case form of a noun can be a circumstance, therefore questions of circumstance are asked for these forms (see below) |
| adjunction (dependent word is an invariable part of speech!): listen carefully, go without looking back, soft-boiled egg |
1. infinitive 2. gerund 3. adverb 4. possessive pronouns (his, her, them) |
1. what to do? what to do? 2. What are you doing? having done what? 3. how? Where? Where? where? When? For what? Why? |
Distinguish!
Her coat is adjoining (whose), to see her is control (whom).
In the categories of pronouns, two homonymous (the same in sound and spelling, but different in meaning) categories are distinguished. The questions of indirect cases are answered by the personal pronoun, and it participates in the subordinating connection - control, and the possessive answers the question whose? and is immutable, it participates in adjacency.
Go to the garden - management, go there - adjoining.
Distinguish between the prepositional case form and the adverb. They may have the same questions! If there is a preposition between the main word and the dependent, then you have control.
Algorithm of actions No. 1.
1) Identify the main word by asking a question from one word to another.
2) Determine the part of speech of the dependent word.
3) Pay attention to the question you ask to the dependent word.
4) According to the identified signs, determine the type of connection.
Parsing the task.
What type of connection is used in the phrase CAPTURE MECHANICALLY.
We define the main word and ask a question from it: catch (how?) mechanically; catch - main word, mechanically - dependent. Determine the part of speech of the dependent word: mechanically- is an adverb. If the dependent word answers the question How? and is an adverb, then the phrase uses the connection abutment.
Algorithm of actions No. 2.
1. In the text, it is easier for you to find the dependent word first.
2. If you need agreement, look for the word that answers the question Which? whose?
3. If you need control, look for a non-nominative noun or pronoun.
4. If you need to find an adjunction, look for an invariable word (infinitive, gerund, adverb or possessive pronoun).
5. Determine from which word you can ask a question to the dependent word.