Security of material reserves with own funds. Coefficient of provision with own working capital stocks
Enterprise sustainability indicators
These indicators are based on the fact that almost any enterprise operates not only on the basis of its own funds, but also on loans or simply temporarily located in the company. A typical case is accounts payable - debts to the budget or to suppliers for goods already received but not paid for.
Ratio of own and borrowed funds
To calculate this indicator, the formula is used:
SC: ZK, where
The value of this coefficient must be at least 0.7, that is, it is considered normal that there are more borrowed funds than own ones. But it is very dangerous to exceed this coefficient - such a situation means that the owners themselves own little in the company. In the event that creditors demand immediate repayment of debts, there will be nothing to repay debts, except for the property of the company, and then nothing will remain of the company.
In the example, the indicators are as follows:
At the beginning of the year - 29,705: (3,000 + 11,195) = 2.09;
At the end of the year - 30,655: (3,000 + 13,460) = 1.86.
This means that the vast majority of a firm's production is controlled by its own owners.
1.3.2 Coefficient of autonomy. This ratio is also called the financial independence ratio. To calculate it, the entire equity capital (line 490 of the Balance) is divided by the total capital of the company (line 700 of the Balance, the final one, sometimes called the “Balance currency”). Autonomy must be greater than 0.5.
In the example:
At the beginning of the year - 29,705: 43,900 = 0.68;
At the end of the year - 30,655: 47,115 = 0.65.
The performance is very good, the enterprise is completely independent.
The inverse indicator is the coefficient of financial dependence. What is considered here is not how independent the company is, but vice versa - how dependent on others.
Financial dependency ratio
The formula is used to calculate:
ZO: OK, where
ZK - the sum of long-term and short-term liabilities (the sum of lines 590 and 690 of the Balance - lines 640 and 650).
OK - the entire capital of the company as a whole (line 700 of the Balance).
Since this indicator is the inverse of the autonomy coefficient, it should not exceed 0.5, otherwise the amount of debts will exceed the amount of the company's own property.
At the beginning of the year - (3000 + 11,195): 43,900 = 0.32;
At the end of the year - (3000 + 13,460): 47,115 = 0.35.
Quite acceptable figures. By the end of the year, the company's debts increased, but this is not critical.
Inventory coverage ratio with own working capital
This indicator is interesting because it allows you to determine whether the company buys raw materials for production at its own expense or not. In other words, will the firm be able to continue production if it is not given a loan.
Formula for calculation:
(SK - VNO): ZP, where
SC - equity (line 490 of the Balance);
ZP - stocks (line 210 of the Balance).
In the given example:
At the beginning of the year - (29,705 - 13,490): 19,200 = 0.84;
At the end of the year - (30,655 - 14,995): 20,100 = 0.78.
Here the company is doing a little worse than in general. Completely deliveries of raw materials and materials are not closed, some of them are purchased at the expense of credits and loans. And this figure has deteriorated over the year. By itself, it is not critical, and the rest of the indicators are good. Therefore, you should just pay attention to this fact and remember it.
Financial stability ratio
The ratio of financial stability is the ratio of the amounts of the company's own capital and its long-term loans to the sum of the Balance total ("Balance currency").
(line 490 of the Balance + line 590 of the Balance) : line 700 of the Balance.
It is believed that it is very profitable for an enterprise to have long-term obligations, since they will not have to be paid off soon, and therefore, in the short term, long-term obligations can be conditionally considered as their own funds. Thus, the presence of a large number of long-term loans at the current time only strengthens the financial stability of the company.
At the beginning of the year - (29,705 + 3,000): 43,900 = 0.74;
At the end of the year - (30,655 + 3,000): 47,115 = 0.71.
The financial stability ratio for this balance sheet is very high.
Permanent asset index
The essence of this indicator is that we find out what part of our own capital is our non-current assets. For this, the formula is used:
VNO: SC, where
VNO - non-current assets (line 190 of the Balance);
At the beginning of the year - 13,490: 29,705 = 0.45;
At the end of the year - 14,995: 30,655 = 0.49.
These are good enough indicators. They mean that a company can use its own capital to purchase raw materials, pay for the work of employees, that is, fully organize work without resorting to borrowings and loans.
The reverse indicator is the percentage of working capital.
Agility factor
They count it like this:
(SK - VNO): SK, where
VNO - non-current assets (line 190 of the Balance);
SC - equity (line 490 of the Balance).
When non-current assets are deducted from equity, current assets remain.
At the beginning of the year - (29,705 - 13,490): 29,705 = 0.55;
At the end of the year - (30,655 - 14,955): 30,655 = 0.51.
The higher this coefficient, the easier it is for the firm to maneuver its resources.
Non-current assets are primarily fixed assets and intangible assets. This property is durable, long-term, acquired once and for many years. And current assets are stocks, receivables, money, securities, that is, what comes quickly and leaves no less quickly. Turning money into raw materials, raw materials into receivables, and then back into raw materials can be done very quickly. This is the effect of maneuverability. The more resources an enterprise has to maneuver, the more stable it is.
In the analysis of the production and economic activities of any enterprise, an important role is played by the calculation of coefficients that affect its financial stability, the ability to quickly respond to changes in the industry, the creditworthiness and liquidity of the company. The equity ratio also belongs to this category.
What it means, how it is calculated and how its changes affect the financial life of the company, we will learn from this article.
Equity Ratio: Definition
The production of each enterprise necessarily involves its own working capital, i.e. capital, which is the property of the company. Their presence in sufficient volume is one of the main conditions for financial freedom and stability of the company in the industry. And, conversely, the absence of such capital is evidence that the current assets of the enterprise (and sometimes part of the production fixed assets) are formed at the expense of borrowed funds and, if the creditor (bank) suddenly wants to withdraw them, the organization will face financial collapse if timely measures are not taken. measures.
How to calculate?
This indicator, which characterizes the availability and sufficiency of own funds, determines the ratio of the share of these assets in the total volume of the company's working capital. At the end of each reporting period, to analyze the situation, the equity ratio is calculated. The formula is:
K cos \u003d C os /A, where C os - working capital, A - the corresponding assets of the company.

The size of С os is calculated by reducing the amount of equity capital by the value of non-current assets (fixed assets and intangible assets) according to the formula:
C os \u003d K - A vn
In relation to the current edition of the balance sheet form, the formula for calculating the coefficient looks like this:
K cos \u003d (balance line (BO-1) 1300 - line BO-1 1100) / line BO-1 1200
Standard
The normal value set for the coefficient at the legislative level is > 0.1, i.e. 10% of the company's total assets and is considered one of the criteria for assessing an unfavorable balance sheet structure, along with other calculated indicators. 10% is the minimum, already critical value, acceptable for the amount of own funds in the property of the organization. It shows the presence or occurrence of problems - a critical level of sufficiency of own funds, low solvency and general destabilization of the enterprise.
Meaning and conclusions based on the results of calculations
The equity ratio assesses the state of the organization in terms of its solvency.

If the value of the coefficient at the end of the reporting period is below 0.1, then the structure of the company's balance sheet is unsatisfactory, and its condition is close to critical. In this case, the company needs a serious revision of the adopted strategy, the urgent development of urgent measures to increase financial stability, and the identification of negative factors that affected the state of the organization. Sometimes radical measures are needed, for example, a change in management or production profile, the introduction of external management (if the company is a branch of a higher organization), etc. In a word, the calculation of the coefficient entails an in-depth analysis of the actual state of the enterprise's finances, its solvency and effective measures to improve the situation .
Example #1
Calculate the equity ratio on the balance sheet using the following data:
Non-current assets (1st section of the balance sheet - line 1100) - 104,600 thousand rubles.
Working capital (2nd section of the balance sheet - line 1200) - 46,650 thousand rubles.
Capital / reserves (3rd section of the balance sheet - line 1300) - 129,950 thousand rubles.
K cos \u003d (129,950 - 104,600) / 46,650 \u003d 0.54
Based on the result of the calculations, we can draw the following conclusions:

The value of the coefficient is 5 times higher than the established standard (0.54 - 0.1 = 0.44);
The equity ratio of 0.54 indicates that the equity capital of the organization is 54%, i.e., it exceeds half the value of the property in the company;
Such provision with own funds is typical for sufficient financial stability of the company.
Example #2
Let's calculate the equity ratio of assets based on other data.
Non-current assets (1st section BO-1 - line 1100) - 98,600 thousand rubles.
Revolving funds (2nd section BO-1 - line 1200) - 15,800 thousand rubles.
Capital / reserves (3rd section of BO-1 - line 1300) - 100,000 thousand rubles.
K cos \u003d (100 00 - 98 600) / 15 800 \u003d 0.09
After analyzing the obtained value, the company's economist informs the management and provides the appropriate conclusions:
The value of the coefficient is below the critical mark by 0.01 (0.09 - .01 = - 0.01);
The ratio of reserves with own funds of 0.09 shows a negligible amount of equity in the composition of the assets of the organization - 9%;
Such provision with own funds speaks of a critical situation in the company - an unsatisfactory balance sheet structure, financial instability, insolvency to partners and creditors.

In conclusion, we note that it is necessary to analyze the financial condition of an enterprise on the basis of the values calculated for such an indicator as the equity ratio. The calculation formula is simple, but the correct interpretation of the obtained values will help to take timely measures to eliminate the crisis situation.
Working capital ratio(SOS) shows the sufficiency of the organization's own funds to finance current activities.
Calculation (formula)
According to the Order of the FSFR of the Russian Federation dated January 23, 2001 N 16 "On approval of the "Guidelines for the analysis of the financial condition of organizations", the coefficient is calculated as follows (in the Order he calls the equity ratio):
Security ratio SOS \u003d (Equity capital - Non-current assets) / Current assets
The meaning of this coefficient is as follows. First, in the numerator, the formulas subtract non-current assets from equity. It is believed that the most low-liquid (non-current) assets should be financed from the most stable sources - equity. Moreover, there must still be some part of the equity to finance current activities.
Normal value
This coefficient is not widespread in Western practice of financial analysis. In Russian practice, the coefficient was introduced by the regulatory Decree of the Federal Office for Insolvency (Bankruptcy) dated 12.08.1994 N 31-r and the now inactive Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 20.05.1994 N 498 "On some measures to implement the legislation on insolvency (bankruptcy) of enterprises. According to these documents, this coefficient is used as a sign of insolvency (bankruptcy) of the organization. According to these documents, the normal value of the equity ratio should be at least 0.1. It should be noted that this is a fairly strict criterion that is unique to the Russian practice of financial analysis; it is difficult for most enterprises to achieve the indicated value of the coefficient.
Equity / Balance = p.1300 / p.1700
End of 2013 1930008/3293652=0.586
Early 2013 1634816/2809673=0.582
It characterizes the independence of the enterprise from borrowed funds and shows the share of own funds in the total value of all funds of the enterprise. The normative value is >0.5, which means the level of independence of the VOMZ OJSC enterprise from creditors is normal and, in case of a demand to repay all debts, the enterprise will be able to satisfy them by realizing 42% of equity capital formed from its own sources.
Financial stability ratio
(Equity + Long Term Liabilities) / Balance = (p.1300 + p.1400) / p.1700.
End of 2013 (1930008+91159)/3293652=0.61
Early 2013 (1634816+3912)/2809673= 0.58
The share of funding sources that an enterprise can use for a long time amounted to 61%. Guideline value?80%, i.e. this suggests that the VOMZ OJSC is dependent on external sources of financing and an unstable situation is possible in the future.
Ratio of borrowed and own funds (shoulder of financial leverage)
Borrowed and borrowed sources / Equity = (p.1400 + p.1510) / p.1300.
End of 2013 (91159+152431)/1930008=0.13
Early 2013 (3912+0)/(1634816)=0.002
Shows how many units of borrowed funds account for each unit of own funds. The dynamics by the end of the year is positive, which indicates a greater dependence of the enterprise on investors and creditors. Enterprise Recommended Value< 0,7. На ОАО «ВОМЗ» данный показатель равен 0,13, что говорит о высокой финансовой устойчивости предприятия.
Permanent asset index
Non-current assets / Equity capital = p.1100 / p.1300.
End of 2013 1191181/1930008=0.62
Early 2013 937563/1634816=0.57
The permanent asset index shows what share of the sources of funds provides financing for the non-current assets of the enterprise, i.e. the core is often productive capacity.
Agility factor
Own working capital / Equity capital = (s.1300 - s.1100) / s.1300.
End of 2013 (1930008-1191181)/1930008=0.38
Early 2013 (1634816-937563)/1634816=0.43
Shows what part of own working capital is in circulation, i.e. in the form that allows you to freely maneuver these funds, and which is capitalized. The ratio should be high enough to allow flexibility in the use of the enterprise's own funds.
A decrease in the indicator indicates a possible slowdown in the repayment of receivables or a tightening of the conditions for granting a trade credit on the part of suppliers and contractors. The increase indicates a growing ability to repay current liabilities.
The organization does not use long-term loans and borrowings, since the sum of the maneuverability coefficient and the fixed asset index is equal to one. Own sources cover either fixed or working capital, therefore the sum of fixed assets and non-current assets and own working capital in the absence of long-term borrowed funds is equal to the amount of own funds:
The coefficient of security of current assets with own working capital
Own working capital / Current assets = (p. 1300 - p. 1100) / p. 1200.
End of 2013 (1930008-1191181)/2102471=0.35
Early 2013 (1634816-937563)/1872110=0.37
It characterizes the presence of own working capital of the enterprise, necessary for its financial stability. Normative value =0.1, which indicates the ability of the enterprise to conduct an independent financial policy.
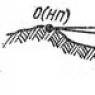
The ratio of the provision of material reserves with own working capital
Own current assets / Stocks = (p.1300 - p.1100) / p.1210.
End of 2013 (1930008-1191181)/ 929 206 =0.79
Early 2013 (1634816-937563)/ 768,646 =0.91
Shows how much of reserves and costs are financed from own sources. It is believed that the coefficient of provision of material reserves with own funds should change within 0.6 - 0.8, i.e. 60-80% of the company's reserves should be formed from its own sources. At the JSC VOMZ enterprise, 79% of the company's reserves are formed from its own sources, which indicates its financial stability.
The coefficient of the real value of fixed assets and material circulating assets in the property of the enterprise
(Fixed Assets + Inventory) / Balance = (line 1150 + line 1210) / line 1600.
End of 2013 (1099172 + 929206)/3293652=0.62
Early 2013 (871401 + 768646)/2809673 = 0.58
Determines what proportion of the value of property is the means of production. Shows what potential the enterprise has in the event of the emergence of new partners and the provision of the production process with the means of production. Based on economic practice data, it is considered normal to limit when the real value of the property is more than 0.5 of the total value of assets. Drawing a conclusion, we can say that the company has a production potential, and it is advisable for suppliers or buyers to enter into an agreement with them.
Drawing a conclusion after analyzing the financial stability of the JSC "VOMZ" enterprise, we can say that it is dependent on external sources of financing, has sufficient autonomy and is able to satisfy the requirements of the creditor to repay debts from its own sources. Also, the financial stability of the enterprise is indicated by 79% of the formed reserves from its own sources and production potential, which is also included in the standard indicators: 0.62.
7. The coefficient of provision of reserves and costs with sources of funds (calculated to determine the type of financial stability)
Koz \u003d (Cob + ∑KiZ) / ISS,
Koz - the ratio of stocks;
Sob - own working capital (Table 6, page 1);
∑KiZ - the amount of credits and loans (Table 5, p. 9);
ISS - sources of own funds (Table 9, page 2).
Koz 08 \u003d (17802 thousand rubles + 5618 thousand rubles) / 23668 thousand rubles = 0.99 = 99%
Koz 09 \u003d (11866 thousand rubles + 5474 thousand rubles) / 23482 thousand rubles = 0.74 = 74%
Goats 10 \u003d (8944 thousand rubles + 23630 thousand rubles) / 26616 thousand rubles = 1.22 = 122%
The calculation results allow us to draw the following conclusions:
1. At the beginning of the period, the financial condition of Askona LLC can be defined as stable, since the ratio of reserves and costs to sources of funds is almost equal to one (0.99), and reserves and costs are slightly more than the amount of own working capital, loans for goods and materials and temporarily free funds.
2. At the end of the period, the financial condition of the enterprise has improved, since inventories and costs are greater than the amount of own working capital, loans for goods and materials and temporarily free funds; the coefficient of provision of reserves and costs with sources of funds is greater than one (1.22), the financial condition of the enterprise can be recognized as absolutely financially stable. The results obtained can be presented in the form of a graph (Appendix 9).
Business activity analysis (productivity and return on assets)
Business activity in a market economy is usually characterized by the effectiveness of financial and economic activities. Such an analysis consists in evaluating the effectiveness of the use of material, financial and labor resources of the organization, in determining the turnover indicators. The results of the analysis show the achieved level of business activity and its impact on the financial stability, competitiveness of the organization, labor efficiency of employees and their quality of life. The most important indicator of the business activity of the organization is labor productivity or output per employee. It characterizes the efficiency of the use of labor resources and is determined by the formula: P \u003d VPT / SCH, where
P - performance;
VPT - revenue (net) of the Profit and Loss Statement;
AMS - the average number of employees for the reporting period.
P 08 \u003d 18,933,600 rubles / 1464 people \u003d 12,932.79 rubles.
P 09 \u003d 29,116,950 rubles / 1531 people \u003d 19,018.26 rubles.
P 10 \u003d 31,300,300 rubles / 1592 people \u003d 19,660.99 rubles.
We can clearly see an increase in labor productivity. As a rule, it is achieved either by increasing the proceeds from the sale of products, works or services, or by reducing the number of personnel of the organization. In our case, the first option takes place, because. The number of employees has been growing year by year.
Another indicator that characterizes the business strategy is the return on assets, which shows the efficiency of using the company's fixed assets. This indicator is calculated based on the balance sheet data (p. 120) and the Profit and Loss Statement (net revenue p. 010) using the formula:
F=st.010/st.120
F 08 \u003d 18933.60 thousand rubles / 46678.00 thousand rubles = 0.40
F 09 \u003d 29116.95 thousand rubles. / 52364.00 thousand rubles = 0.55
F 10 \u003d 31300.30 thousand rubles. / 65350.00 thousand rubles = 0.49
Thus, it can be seen that for each thousand rubles invested in fixed assets in 2008, 2009 and 2010. produced products for 400, 550 and 490 rubles. respectively.
The growth of capital productivity indicates an increase in the efficiency of the use of fixed assets and is regarded as a positive trend. It is achieved by increasing sales proceeds and reducing the value of the residual value of fixed assets. In our case, the return on assets decreased in 2010 compared to 2009, which will undoubtedly be a negative trend.
Profitability analysis
Profit is one of the main sources of formation of financial resources of the enterprise. Profitability, in contrast to profit, showing the result of entrepreneurial activity, characterizes the effectiveness of this activity. The profitability of products can be calculated both for all products sold, and for its individual types:
1) The profitability of all products sold can be defined as:
The percentage of profit from the sale of products to the costs of its production and sale (cost);
Percentage of profit from sales of products to revenue from sales of products;
Percentage of balance sheet profit to revenue from sales of products;
The ratio of net profit to sales revenue.
These indicators give an idea of the effectiveness of the current costs of the enterprise and the degree of profitability of the products sold.
2) The profitability of certain types of products depends on the price and the total cost. It is defined as the percentage of the selling price of a unit of a given product minus its full cost to the full cost of a unit of this product.
3) Profitability of property (assets) of an enterprise is calculated as a percentage of gross (net) profit to the average value of assets (property).
4) The profitability of non-current assets is defined as the percentage of net profit to the average value of non-current assets.
5) Return on current assets is defined as the percentage of net profit to the average annual value of current assets.
6) Return on investment is defined as the percentage of gross profit to the value of the property of the enterprise.
7) Return on equity is defined as the percentage of gross (net) profit to the amount of equity.
Profitability indicators are used in the process of analyzing the financial and economic activities of the enterprise, management decisions, decisions of potential investors on participation in the financing of investment projects.
The main indicator is the profitability of sales. It reflects the return on investment in the main production. It is determined according to the Profit and Loss Statement:
R p \u003d (p.050 / (p.020 + p.030 + 040)) * 100%
It is customary to consider an organization to be highly profitable if P n > 30%, i.e. for every 100 rubles. conditional investments profit exceeds 30 rubles. When P p takes a value from 20 to 30%, the organization is considered highly profitable, in the range from 5 to 20% medium profitable, and in the range from 1 to 5% low profitability.
In our case, the calculation will be as follows:
Rp 08 \u003d (530.1 thousand rubles / (823.2 thousand rubles + 1836.6 thousand rubles + 5178.3 thousand rubles)) * 100% \u003d 6.76%
Rp 09 \u003d (563.3 thousand rubles / (874.65 thousand rubles + 2051.3 thousand rubles + 5601.9 thousand rubles)) * 100% \u003d 6.61%
Rp 10 \u003d (596.4 thousand rubles / (926.1 thousand rubles + 1966.1 thousand rubles + 5625.6 thousand rubles)) * 100% \u003d 7.00%
So, we can observe that our enterprise is averagely profitable, however, by 2010 the profitability indicator has slightly increased, which is a positive trend.
Valuation of capital invested in property
The creation and increment of the property of the enterprise is carried out at the expense of equity and borrowed capital, the characteristics of which are shown in the liabilities side of the balance sheet. To analyze the capital invested in the property of the enterprise, it is advisable to compile Table 3, from which it can be seen that in the analyzed period there was a general increase in the sources of the enterprise's funds by 49,718 thousand rubles. This was due to an increase in equity capital by 14,874 thousand rubles. and borrowed capital for 34848 thousand rubles.
Table 3. Valuation of capital invested in property
| № | Index | Change | ||||||
| Specific weight, % | Specific weight, % | Specific weight, % | ||||||
| 1 | Sources of enterprise funds, total | 80940 | 100 | 89836 | 100 | 130658 | 100 | +49718 |
| 2 | Equity | 64978 | 80,30 | 65638 | 73,06 | 79852 | 61,12 | +14874 |
| 3 | Borrowed capital | 15962 | 19,70 | 24198 | 26,94 | 50806 | 38,88 | +34844 |
| 3.1 | Long term capital | 74 | 42 | 70 | - 4 | |||
| 3.2 | Short term capital | 15888 | 24156 | 50736 | +34848 | |||
| 4 | Funds needed to finance non-current assets | 47176 | 53772 | 70908 | +23732 | |||
| 5 | The amount of own working capital | 17802 | 11866 | 8944 | - 8858 | |||
Looking ahead and analyzing the factors affecting the amount of working capital (Table 6), it can be noted that the increase in equity was due to an increase in additional capital by 7046 thousand rubles, reserve capital by 3630 thousand rubles and retained earnings by 4198 thousand roubles. The share of retained earnings in the total volume of own sources for the analyzed period increased by 2099 thousand rubles. This may indicate an increase in the business activity of the enterprise.
The increase in borrowed capital was due to the growth of short-term liabilities (+34844 thousand rubles), which largely covered the decrease in long-term liabilities (-4 thousand rubles). The change in short-term liabilities, in turn, was caused by an increase in accounts payable (+19,600 thousand rubles). It should be noted that during the analyzed period, accounts receivable increased by 6616 thousand rubles. (Table 2), which is 3 times less than the growth of accounts payable.
When analyzing the capital invested in property, it is necessary to evaluate its structure (Table 4).
Table 4. Capital structure of Askona LLC for 2008-2010
| № | Index | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| 1 | Current assets, % (Table 1, page 2) | 41,62 | 40,10 | 45,68 |
| 2 | Non-current assets, % (Table 1, page 1) | 58,38 | 59,90 | 54,32 |
| 3 | Own capital, % (Table 3, page 2) | 80,30 | 73,06 | 61,12 |
| 4 | Share of coverage of current assets by own capital and long-term borrowed funds (p.3-2) | 21,92 | 13,16 | 6,80 |
When evaluating the structure of an enterprise, the following rule applies: elements of fixed capital, as well as its most stable part of working capital, must be financed from own and long-term borrowed funds; the rest of the current assets, depending on the value of the commodity flow, should be financed by short-term borrowed funds.
In general, the capital structure of Askona LLC at the beginning of the analyzed period corresponds to the rule of optimal capital structure. But in 2009 and 2010 the situation worsens; if at the beginning of the reporting period, own sources and long-term borrowed funds covered non-current assets and 21.92% of current assets, then in 2009 the share of coverage of current assets with equity and long-term borrowed funds decreased to 13.16%, and in 2010 to 6.80%. This happened due to a decrease in the share of equity capital and long-term borrowed capital in the total amount of the enterprise's funds and due to a change in the structure of the enterprise's property as a whole. A negative trend is an increase in the share of short-term borrowed funds of the organization. The change in the capital structure of Askona LLC can be defined as a negative trend in the activity of the enterprise, as this indicates that, in general, during the analyzed period, there was an increase in the dependence of the enterprise on creditors.
Analysis of the security of the enterprise with its own working capital
Normal sources of coverage for inventories, costs and receivables include:
Own capital (due to which own working capital is formed);
Short-term credits and loans;
Trade accounts payable.
To analyze the security of the enterprise with its own working capital, we will compile Table 5, from which it can be seen that the availability of own working capital at the end of 2008 was insufficient to cover stocks, costs and receivables. Lack of working capital may indicate an unstable financial position of our company.
Table 5. Security of the enterprise with its own working capital
| № | Index | Change | |||
| 1 | 17802 | 11866 | 8944 | - 8858 | |
| 2 | Stocks | 23016 | 23120 | 23344 | +328 |
| 3 | Accounts receivable of buyers and customers for goods, works, services | 568 | 1566 | 1204 | +636 |
| 4 | Advances issued | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | Total (line 2+3+4) | 23584 | 24686 | 24548 | +964 |
| 6 | Short-term loans and loans against reserves and costs | - | - | - | - |
| 7 | Accounts payable for goods, works, services | 5618 | 5474 | 23630 | 18012 |
| 8 | Advances received from buyers and customers | - | - | - | - |
| 9 | Total (p.6+7+8) | 5618 | 5474 | 23630 | +18012 |
| 10 | Inventories and costs not credited by the bank | 17966 | 19212 | 918 | - 17048 |
| 11 | Surplus (shortage) of own working capital to cover inventories, costs and receivables | - 164 | - 7346 | 8026 | +8190 |
At the end of 2009 there were significant negative changes, which led to a sharp increase in the lack of working capital in the amount of 7346 thousand rubles. The reason for this was the growth in the volume of inventories and costs not credited by the bank, and the decrease in the volume of own working capital at the enterprise. Growth in surplus inventories and costs uncredited by the bank is due to the fact that the increase in inventories, costs and receivables exceeded the increase in the value of loans and borrowings.
In 2010 there was an increase in accounts payable (+19,600 thousand rubles). The reason for this growth was a sharp increase in the company's debt to pay dividends to its founders. By the end of the year, the enterprise has an excessive amount of own working capital to cover inventories, costs and receivables, which indicates the normal financial stability of the joint-stock company.
Since at the beginning of the period there is a lack of own working capital to cover inventories, costs and receivables, it is necessary to analyze the influence of various factors on their value (Table 6).
Table 6. Analysis of factors affecting the amount of own working capital
| № | Index | Change | |||
| 1 | Availability of own working capital | 17802 | 11866 | 8944 | - 8858 |
| 2 | Influence of factors | ||||
| 2.1 | Authorized capital in terms of the formation of working capital | - 22172 | - 28768 | - 45904 | - 23732 |
| 2.2 | Extra capital | 23562 | 30608 | 30608 | +7046 |
| 2.3 | Reserve capital | 4470 | 6212 | 8100 | +3630 |
| 2.4 | Retained earnings (uncovered loss) | 11942 | 3814 | 16140 | +4198 |
The data presented in Table 6 allow us to draw the following conclusions:
1. In the reporting period, the value of non-current assets increased by 23,732 thousand rubles, therefore, there is a negative trend in the change in the authorized capital in terms of the formation of working capital: in 2008, its shortfall was 22,172 thousand rubles, in 2009 it increased to 28,768 thousand rubles, by the end of 2010 increased by 17136 thousand rubles. and amounted to 45904 thousand rubles.
2. Additional capital in the period under review increased by 7046 thousand rubles. and amounted to 30608 thousand rubles.
3. The amount of reserve capital for the analyzed period increased by 3630 thousand rubles.
4. By the beginning of 2009, retained earnings decreased significantly and amounted to 3814 thousand rubles, against 11942 thousand rubles. last year. At the end of 2010, the value of this indicator increased by 12,326 thousand rubles. and amounted to 16140 thousand rubles.
The total influence of the factors amounted to 8858 thousand rubles, which is the amount of the decrease in own working capital (Table 6, page 1).
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the use of working capital in the enterprise
The main characteristic of working capital (in addition to cost and structure) is the efficiency of their use. The following indicators of the efficiency of the use of working capital are distinguished:
Working capital turnover ratio;
Working capital utilization factor;
Duration of one turn in days;
The amount of released or additionally attracted working capital.
The calculated data of these indicators are presented in Table 7.
Table 7. Analysis of the effectiveness of the use of working capital
| № | Index | Change | |||
| 1 | Sales volume | 254654 | 337956 | 361554 | +106900 |
| 2 | Number of days in the reporting period | 360 | 360 | 360 | |
| 3 | One-day turnover of product sales (calculation) | 707,37 | 938,77 | 1004,32 | +296,95 |
| 4 | Average value of balances | 33690 | 36022 | 59680 | +25990 |
| 5 | Working capital turnover ratio (calculation) | 7,56 | 9,38 | 6,06 | - 1,5 |
| 6 | Working capital utilization factor (reverse page 5) | 0,13 | 0,11 | 0,17 | +0,04 |
| 7 | Duration of one revolution in days (calculation) | 47,61 | 38,38 | 59,41 | +11,80 |
Calculation for filling the table:
OO - one-day turnover of product sales;
D - duration of the analyzed period.
OO 08 \u003d 254654 thousand rubles. / 360 days = 707.37 thousand rubles
OO 09 \u003d 337956 thousand rubles. / 360 days = 938.77 thousand rubles
OO 10 \u003d 361554 thousand rubles. / 360 days = 1004.32 thousand rubles
K about. =Q p / Q cp ,
K about. - turnover ratio of working capital;
Q p - sales volume;
To ob.08 \u003d 254654 thousand rubles. / 33690 thousand rubles = 7.56
To ob.09 \u003d 337956 thousand rubles. / 36022 thousand rubles = 9.38
To ob.10 = 361554 thousand rubles. / 59680 thousand rubles = 6.06
K s \u003d Q cp / Q p,
K h. - working capital utilization factor;
Q p - sales volume;
Q cp - the average cost of the balances.
To z.08 \u003d 33690 thousand rubles. / 254654 thousand rubles = 0.13
To z.09 = 36022 thousand rubles. / 337956 thousand rubles = 0.11
To z.10 = 59680 thousand rubles. / 361554 thousand rubles = 0.17
ON=D/K about. ,
ON - the duration of one revolution in days;
D - duration of the analyzed period;
K about. - turnover ratio of working capital.
ON 08 = 360 days / 7.56=47.61 days
ON 09 = 360 days / 9.38=38.38 days
PO 10 = 360 days / 6.06=59.41 days
In the analyzed period, there was an increase in the volume of sales by 106,900 thousand rubles. and the average cost of working capital balances by 25,990 thousand rubles. These changes have had the following impact on the efficiency of the use of working capital:
1. There was an increase in the one-day turnover of product sales by 296.95 thousand rubles. This can be defined as a positive trend in the activities of the enterprise.
2. The turnover ratio at the beginning of 2010 decreased by 1.5 compared to 2008. This suggests that if at the beginning of the period under review one ruble of working capital brought 7.56 rubles. of sold products, then at the beginning of 2009 this value amounted to 9.38 rubles, by the end of the reporting period 0.06. In other words, working capital makes 6.06 turnovers, which is 1.5 turnovers less than at the beginning of the study period.
3. The working capital utilization rate for the analyzed period increased by 0.04 and amounted to 0.17, that is, if at the beginning of the year to receive 1 rub. sold products required 0.13 rubles. working capital, then by the end of the year this value increased and amounted to 0.17 rubles. This can be defined as a negative trend in the use of working capital.
4. There were significant fluctuations in the duration of one turnover in days from 47.61 days in 2008 to 38.38 days in 2009 and 59.41 days in 2010, that is, by 11.80 days, which, in in turn, is a negative trend in the use of working capital.
When analyzing working capital, it is necessary to evaluate the influence of factors on the turnover rate of working capital.
Kob \u003d Q p / Q cp,
Cob - turnover ratio of working capital;
Q p - sales volume;
Q cp - the average cost of the balances.
As a result of an increase in the volume of sales by 106,900 thousand rubles. and an increase in the average cost of working capital balances by 25,990 thousand rubles. the turnover ratio in the reporting period decreased by 1.5, which was a negative trend in the use of working capital.
It should be noted that during the analyzed period there were negative changes in most indicators characterizing the efficiency of the use of working capital. Therefore, we can conclude that there is a general trend towards a decrease in the efficiency of the use of working capital.
General conclusions on the assessment of the financial condition of Askona LLC
Based on the analysis of the financial condition of the organization, we can conclude that Askona LLC is in a difficult situation. Namely, by 2010 the critical and current liquidity ratios are below the normative values, which indicates the company's inability to repay its debts to creditors.
Also, a negative point is the decrease in the coefficients of financial stability, equity capital agility and financial independence. This suggests that the largest share in the total amount of funding sources is occupied by borrowed funds.
Also, the growing accounts receivable and accounts payable cannot be called a positive trend, which indicates insufficient work to strengthen the settlement and payment discipline in the organization.
But, despite these changes, for some indicators there has been a trend towards improvement, namely, increased sales revenue (Table 7, page 1), - in 2008 it amounted to 254,654 thousand rubles, in 2009 - 337,956 thousand .rub., in 2010 361,554 thousand rubles, although the cost increased. It is important to note that this is due to an increase in tailoring for third-party organizations, and not an increase in the production of own products.
Conditions or deviations in the implementation of the plan should be analyzed. The plan, if appropriate, should be adjusted. The use of modern management decision support technologies allows the organization and its manager to carry out the planning process more efficiently. 14. Monitoring the implementation of the plan. Ensuring the effective operation of the organization involves continuous ...
It also comes down to summarizing the results of a study of profits and expenses for a specific type of transportation, work or service. 1.2 Goals, objectives and information base for evaluating the effectiveness of an enterprise The information support of the analysis reflects the whole set of simultaneously or sequentially performed operations that cause the process of accelerating the development of economic ...
Avoid mistakes. For impulsive, for example, the opposite tactical line is characteristic: they are guided by success and are less sensitive to failures /3, p.202,203/ traditionally high quality products and culture of production. 28 ...